| 2-Amino-5-(ethylthio)-1,3,4-thiadiazole | 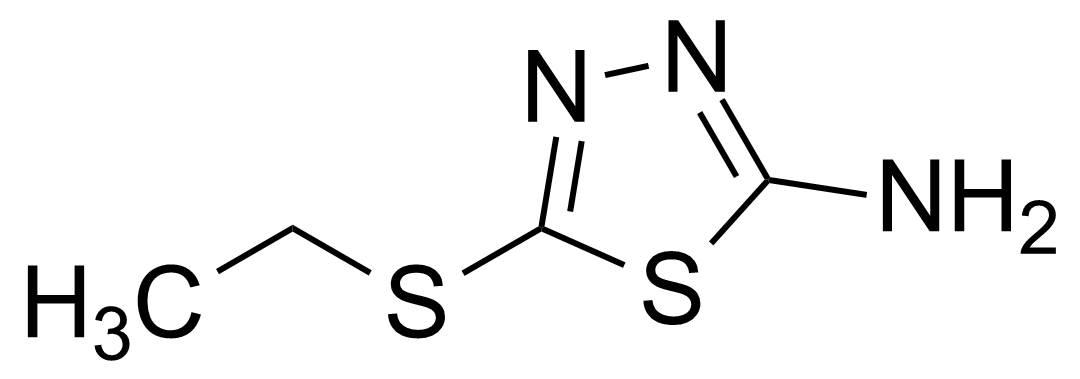 | [25660-70-2] | GEO-00136 |
| 6-Amino-2-mercaptobenzothiazole | 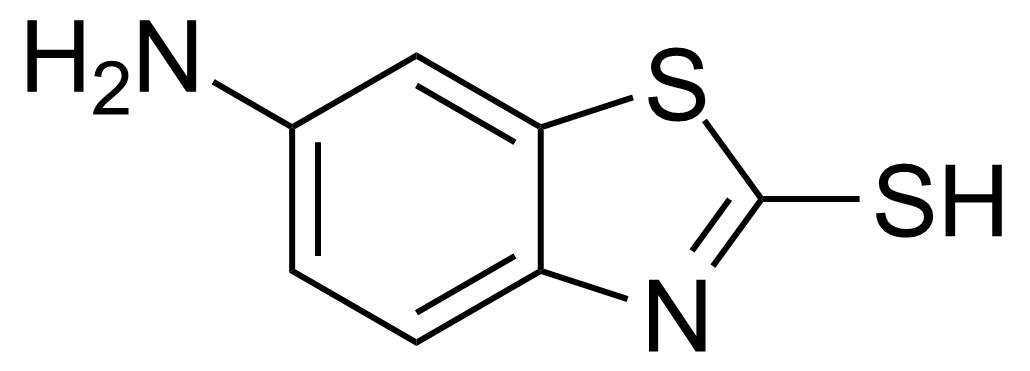 | [7442-07-1] | GEO-00151 |
| 4-Amino-2-mercaptopyrimidine | 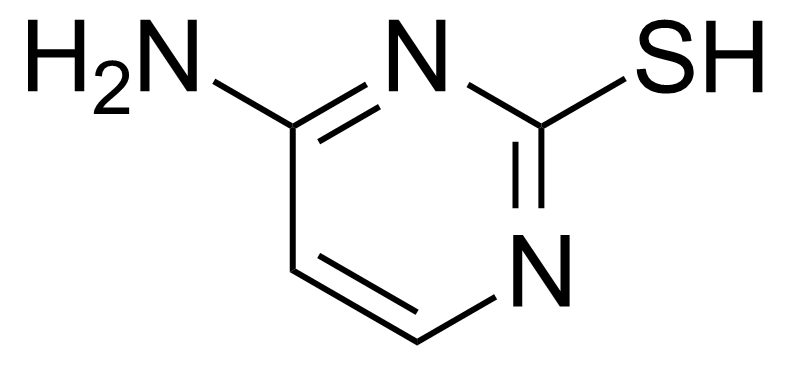 | [333-49-3] | GEO-00152 |
| 2-Amino-5-(methylthio)-1,3,4-thiadiazole | 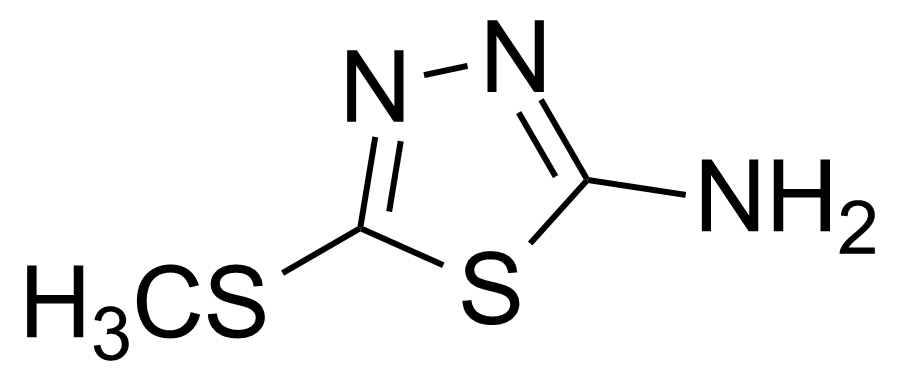 | [5319-77-7] | GEO-00174 |
| New | 6-Anilino-1,3,5-triazin-2,4-dithiol monosodium salt | 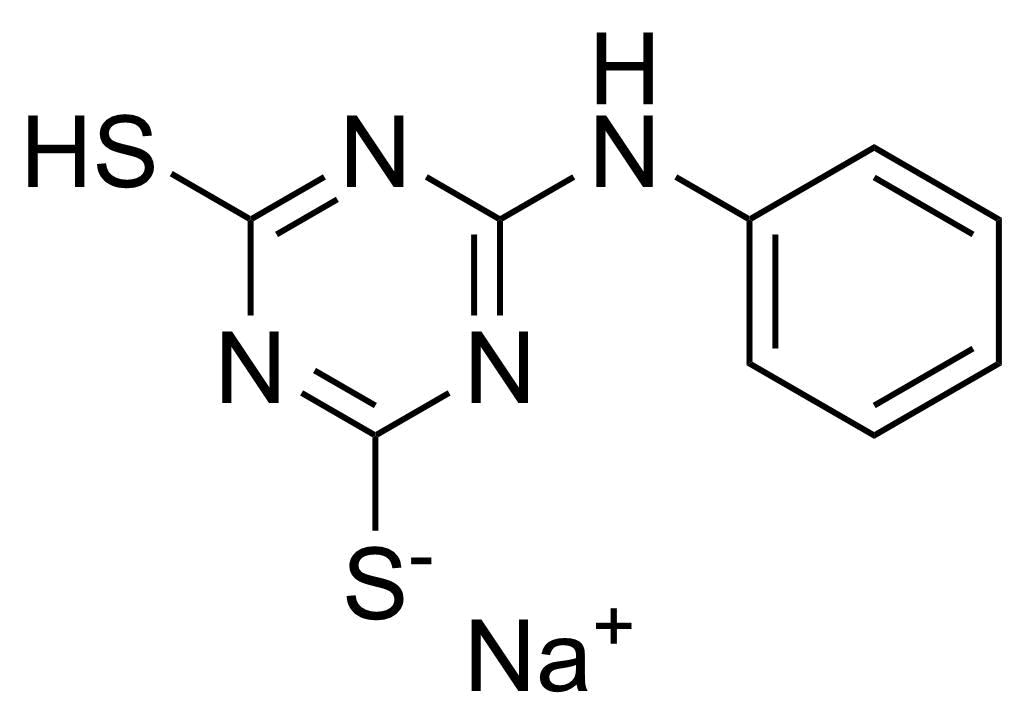 | [57343-38-1] | GEO-04839 |
| New | 1,3-Benzenedithiol | 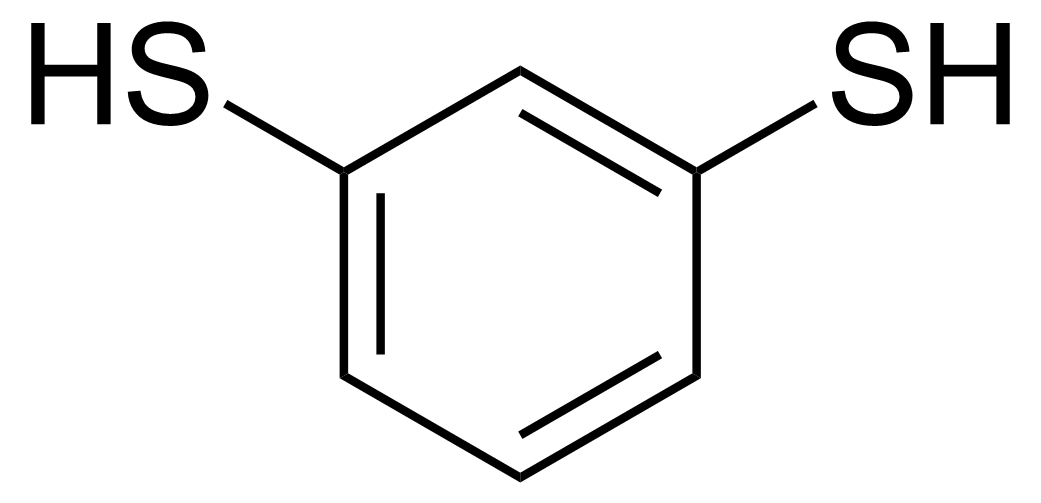 | [626-04-0] | GEO-03897 |
| Benzene-1,4-dithiol | 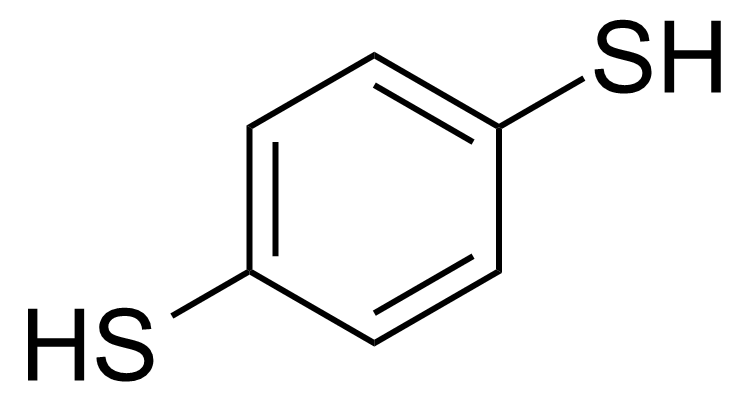 | [624-39-5] | GEO-04155 |
| 1,2-Benzenedithiol | 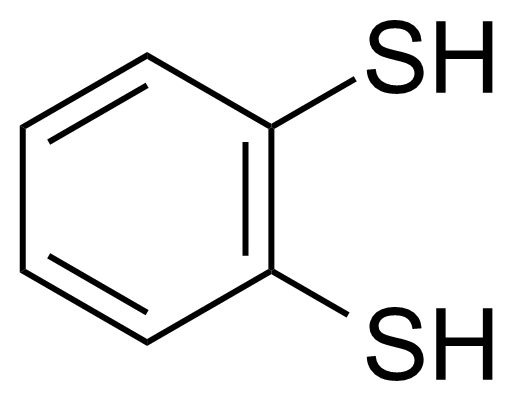 | [17534-15-5] | GEO-00251 |
| 4-Benzylthio-1H-pyrazole | 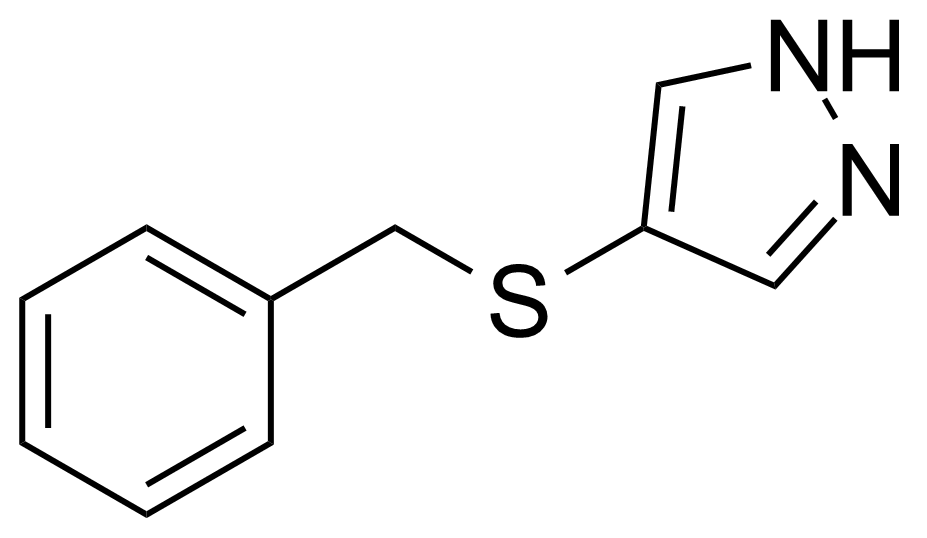 | [308121-87-1] | GEO-04063 |
| 5-Bromo-1,3-benzenedithiol | 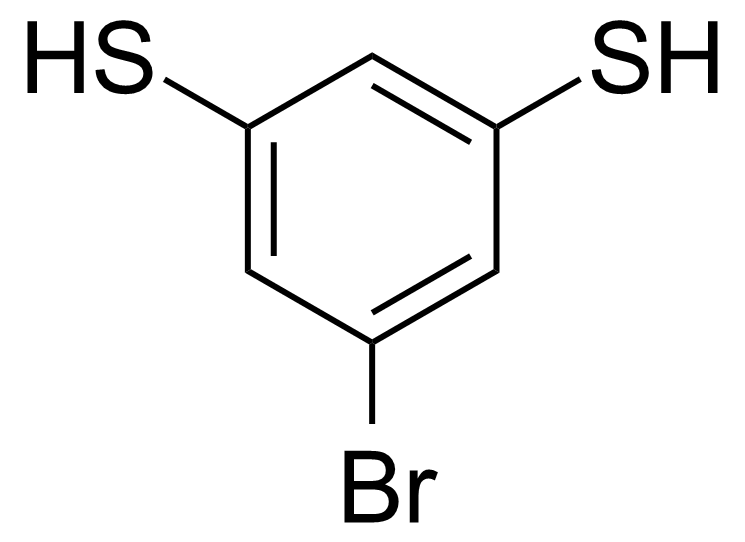 | [1219501-75-3] | GEO-04125 |
| 2-Bromo-4-fluoro-1-(methylthio)benzene | 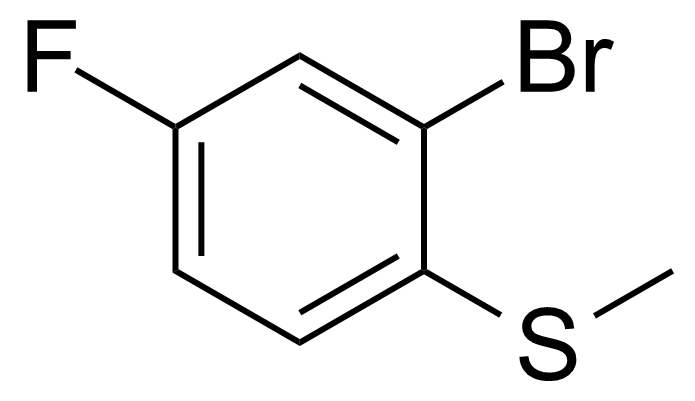 | [91524-70-8] | GEO-04054 |
| (4-Bromophenyl)diphenylsulfonium triflate | 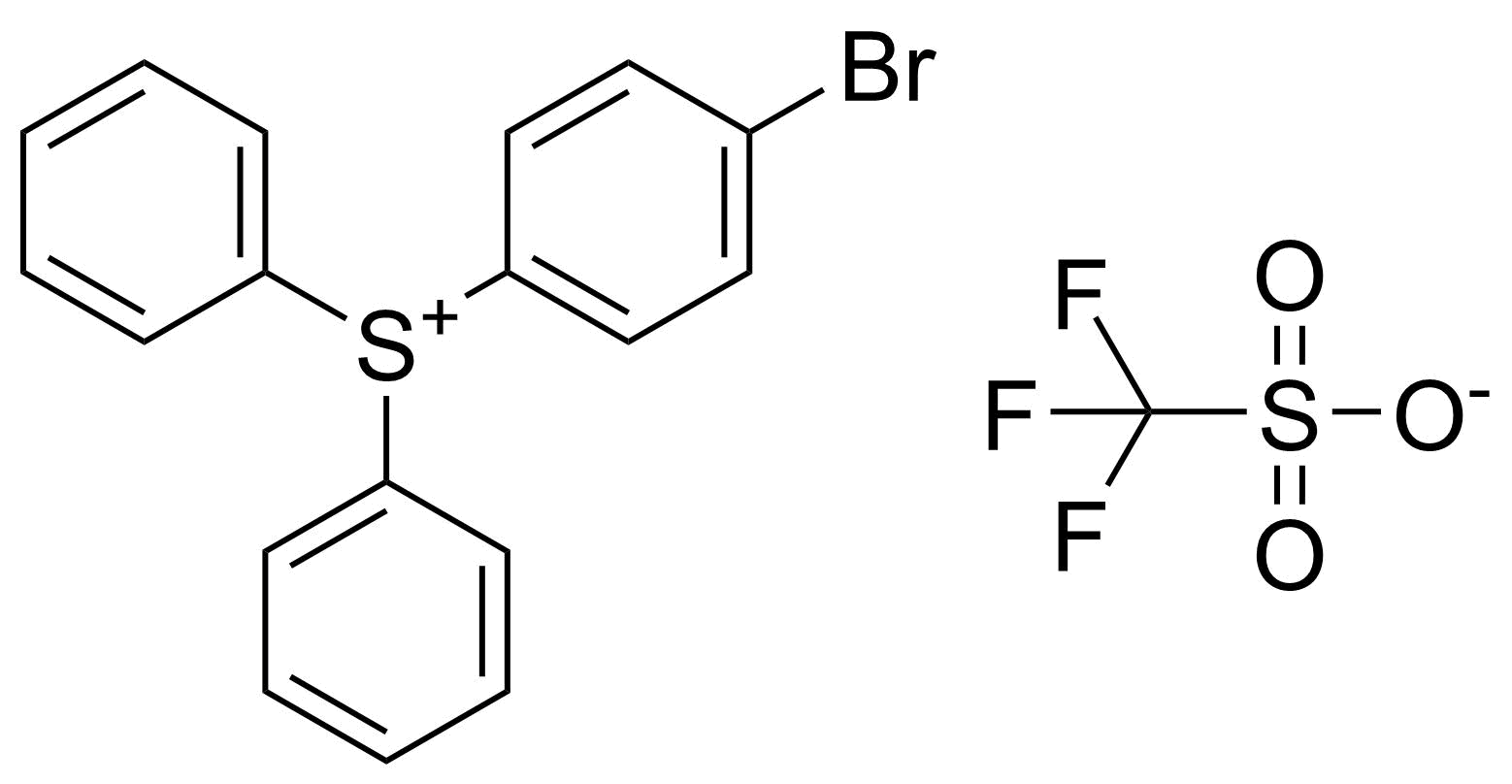 | [255056-44-1] | GEO-04499 |
| 2-(tert-Butyl)benzenethiol | 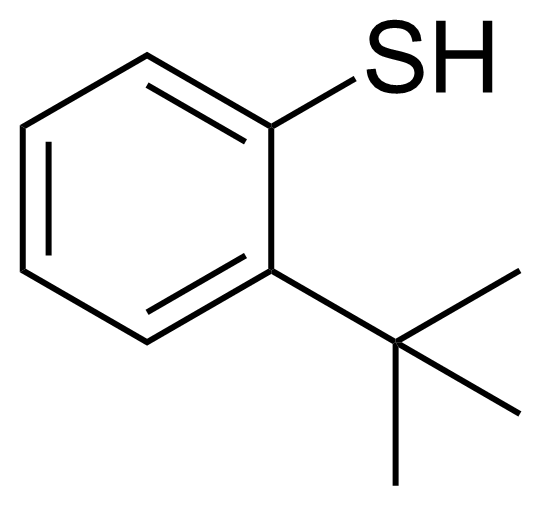 | [19728-41-7] | GEO-04077 |
| 5-tert-Butyl-2-hydroxy-3-(methylthio)benzaldehyde |  | [81322-70-5] | GEO-02513 |
| 2-Chloroethyl ethyl sulfide | 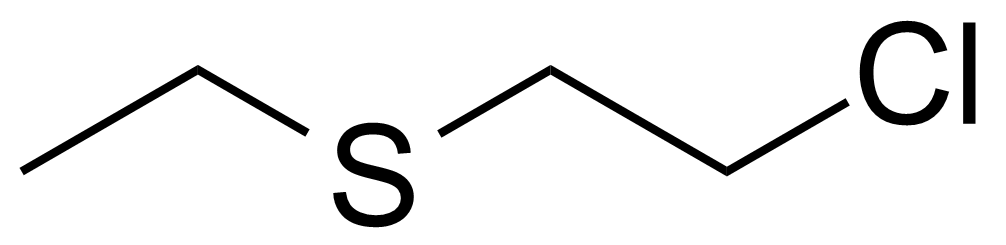 | [693-07-2] | GEO-03411 |
| 5-Chloro-3-methylmercapto-1,2,4-thiadiazole | 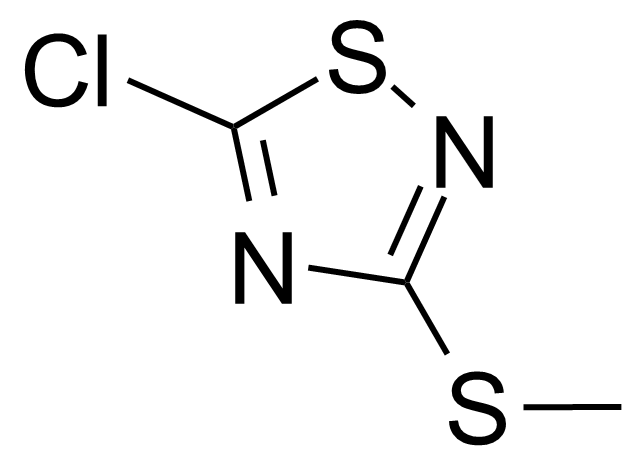 | [21735-15-9] | GEO-02726 |
| 2-Chloro-6-methylthiophenol | 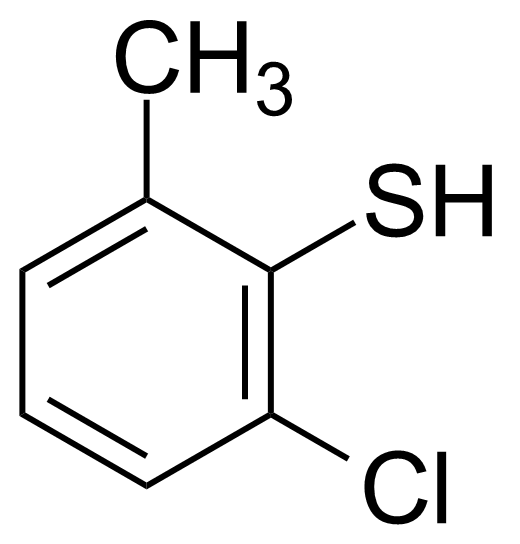 | [18858-05-4] | GEO-00733 |
| (3-Chlorophenyl)methanethiol | 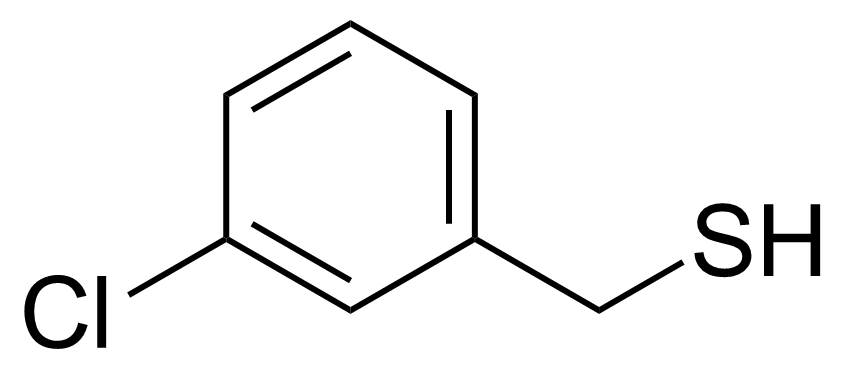 | [25697-57-8] | GEO-00766 |
| Cyanomethyl-2,3,4,6-tetra-O-acetyl-a-D-thiomannopyranoside | 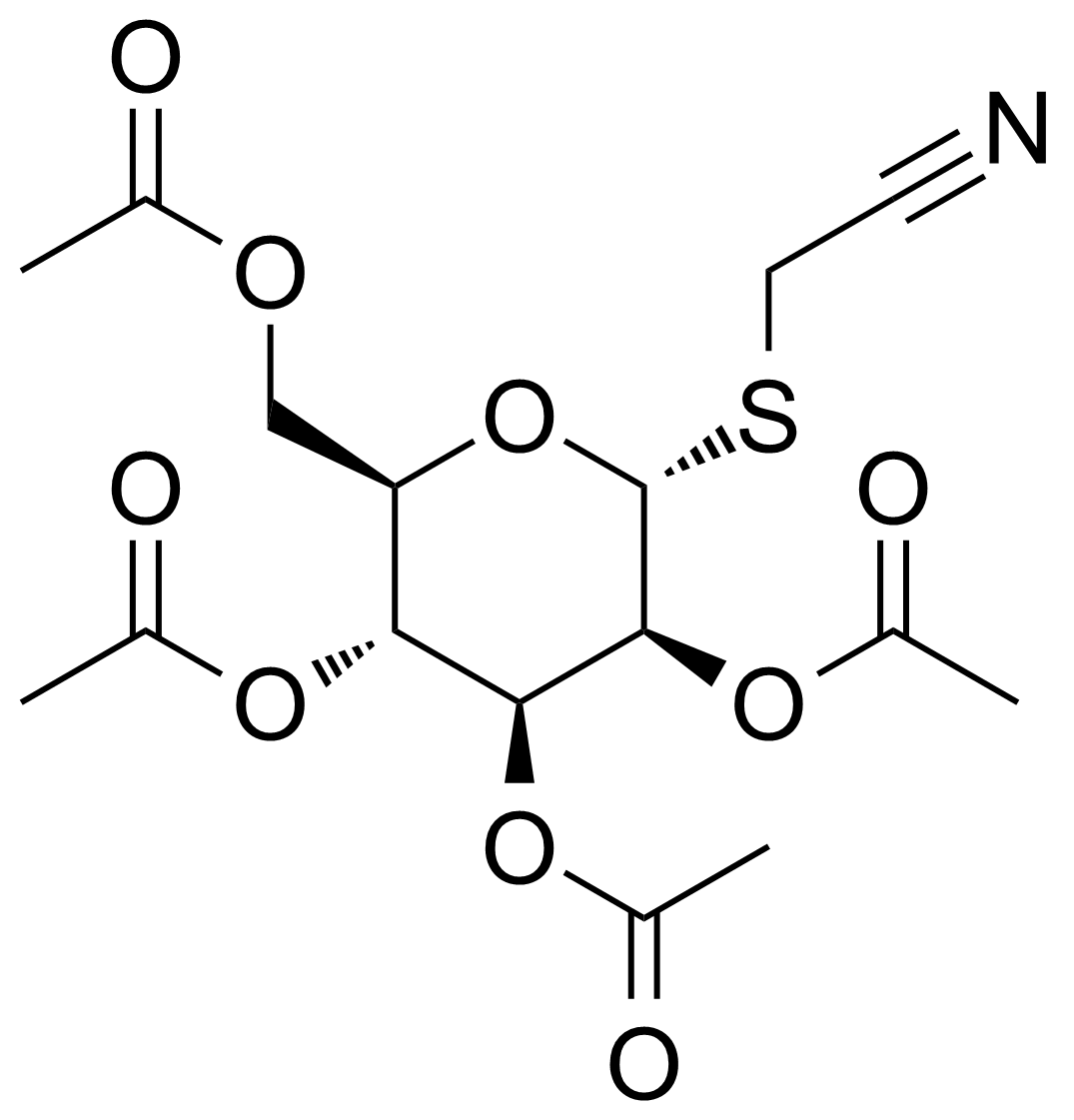 | [61145-39-9] | GEO-04234 |
| Cyclohexene sulfide | 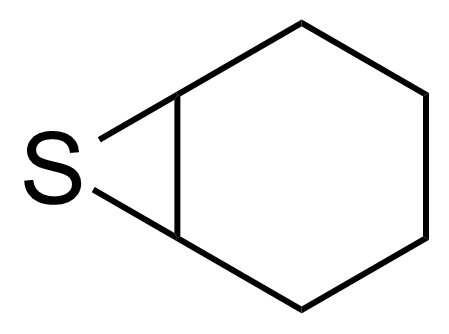 | [286-28-2] | GEO-00868 |
| 4-Cyclopentylamino-2-methanethiopyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester | 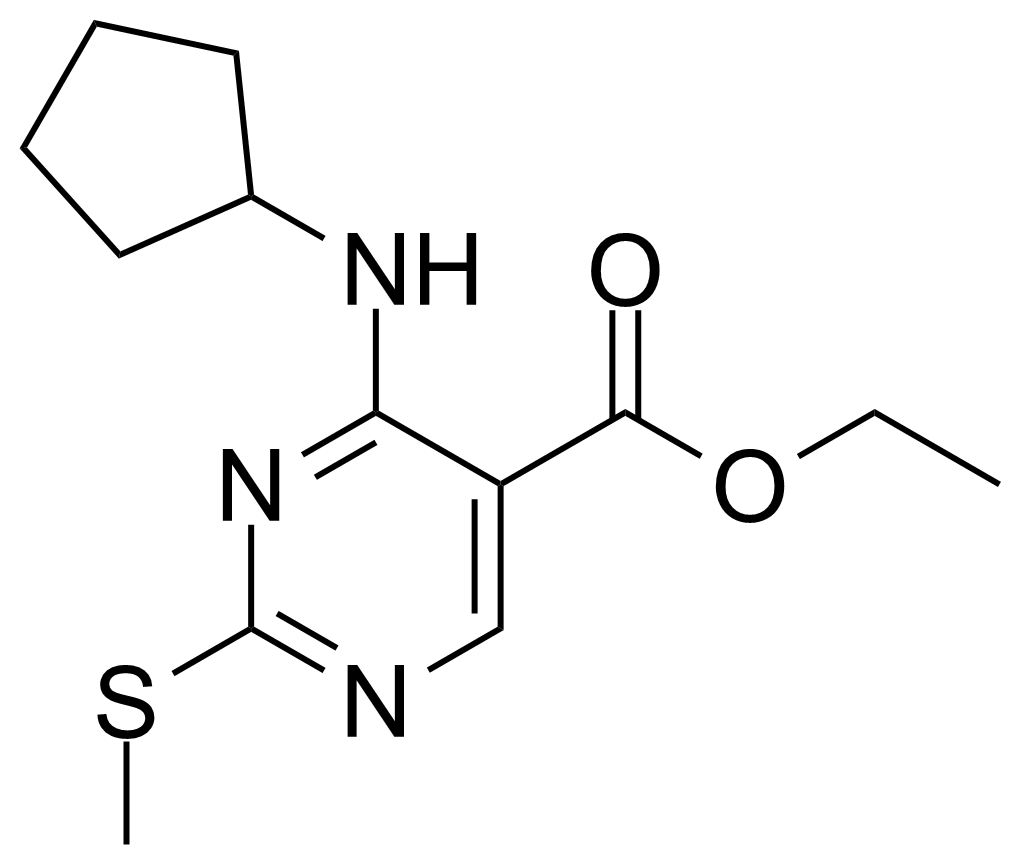 | [211245-62-4] | GEO-04295 |
| 4,6-Diamino-2-mercaptopyrimidine | 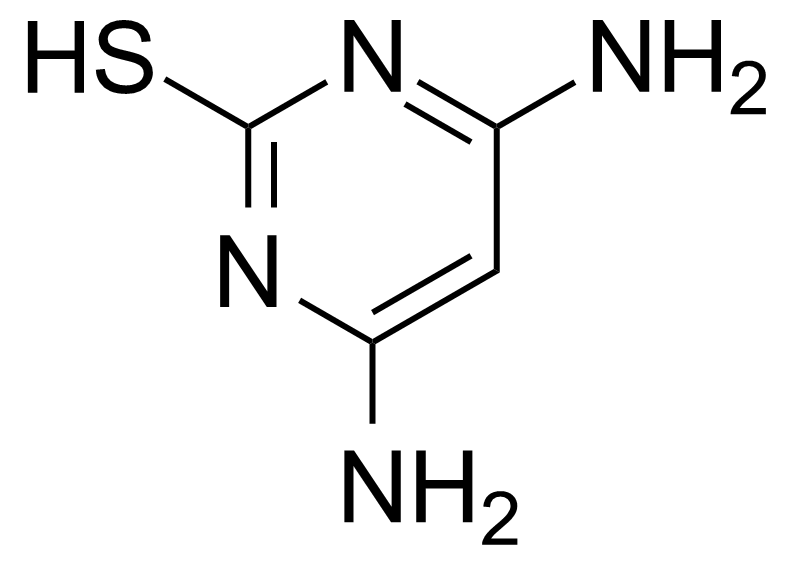 | [1004-39-3] | GEO-00921 |
| 3,5-Dichlorobenzenemethanethiol | 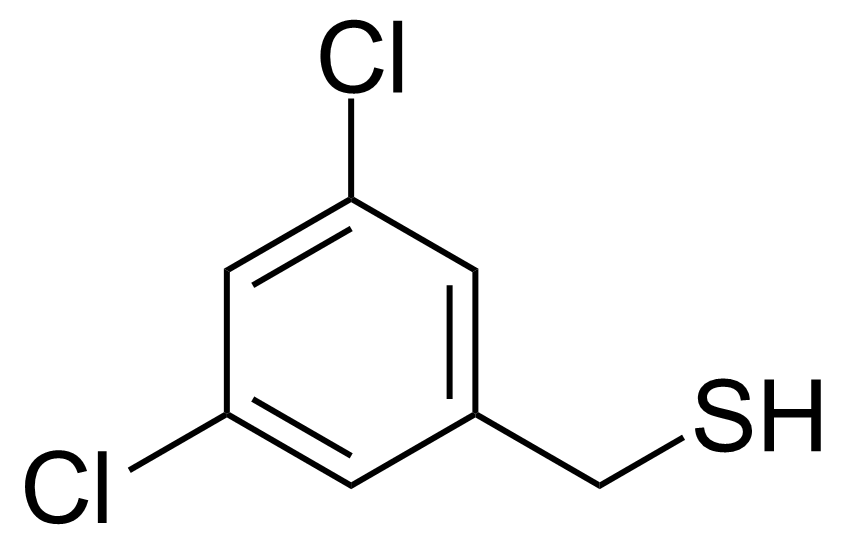 | [65963-17-9] | GEO-03033 |
| Diethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(5-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate |  | N/A | GEO-03540 |
| (3,4-Difluorophenyl)methanethiol | 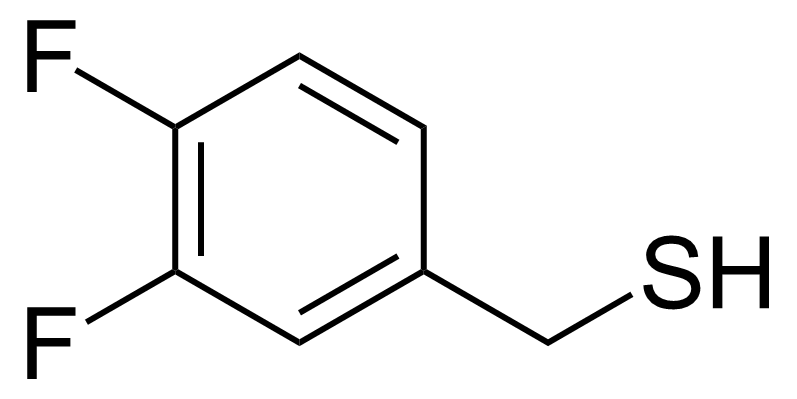 | [666752-97-2] | GEO-01068 |
| (2,5-Difluorophenyl)methanethiol | 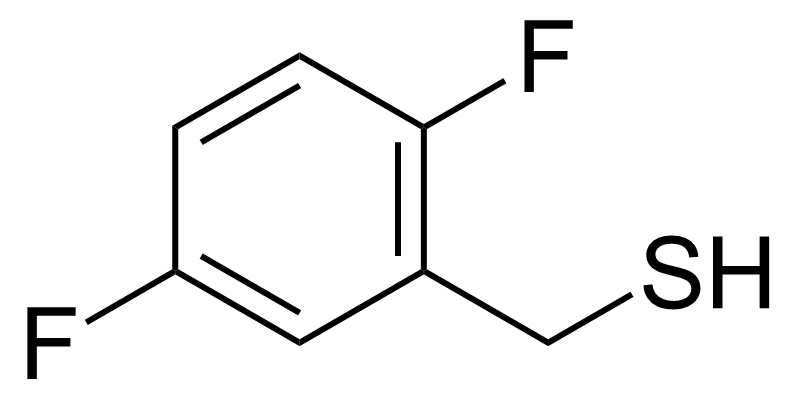 | N/A | GEO-01067 |
| (2,4-Difluorophenyl)methanethiol | 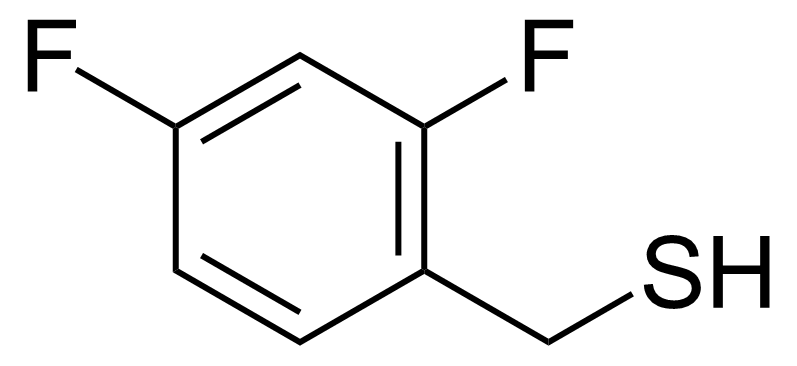 | [170924-51-3] | GEO-01066 |
| 5,6-Dihydro-1,4-dithiin-2,3-dicarboximide | 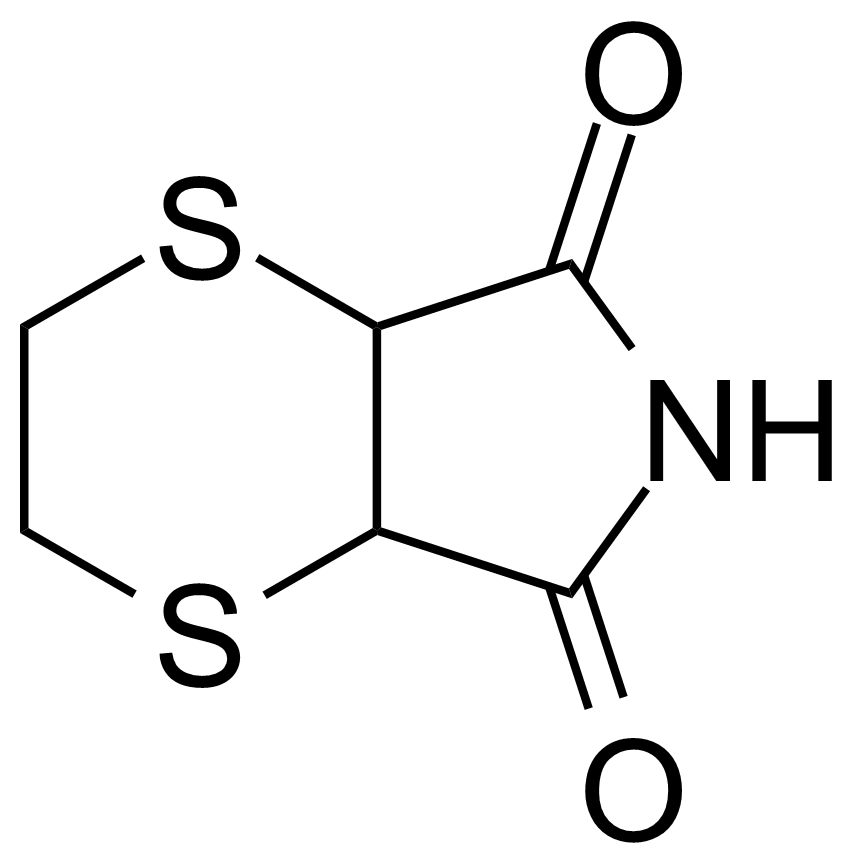 | [24519-85-5] | GEO-01089 |
| 2,3-Dihydro-1,4-dithiino[2,3-c]furan-5,7-dione | 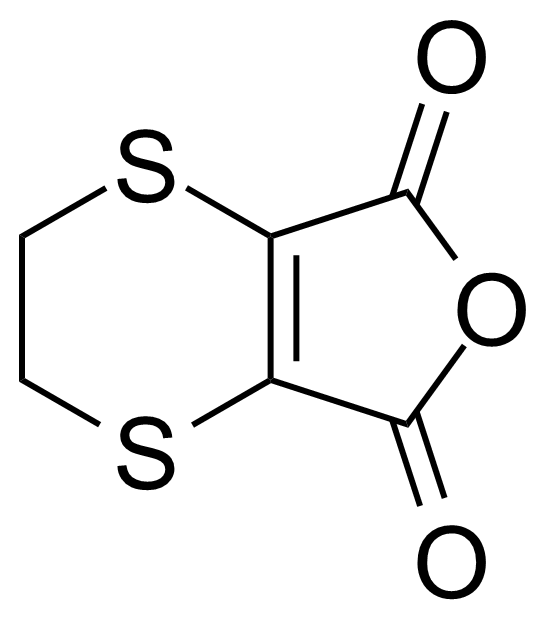 | [10489-75-5] | GEO-01087 |
| 4,6-Dihydro-1H,3H-thieno[3,4-c]furan-1,3-dione |  | [75532-25-1] | GEO-04022 |
| 2,5-Dihydrothiophene-3,4-dicarboxylic acid | 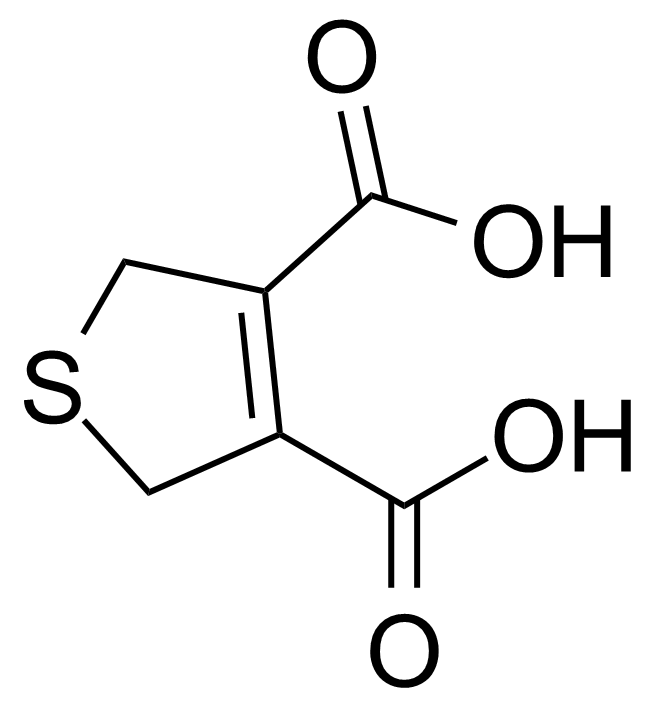 | [20688-07-7] | GEO-04023 |
| New | 3,4-Dimercaptotoluene | 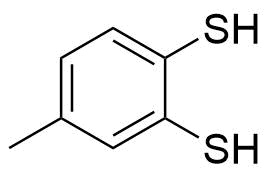 | [496-74-2] | GEO-03465 |
| 1-(Dimethylamino)-2-propanethiol | 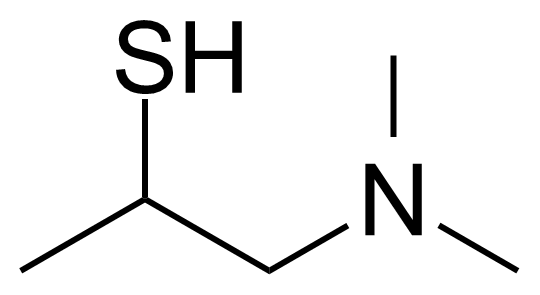 | [1920-46-3] | GEO-03732 |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)-1-propanethiol | 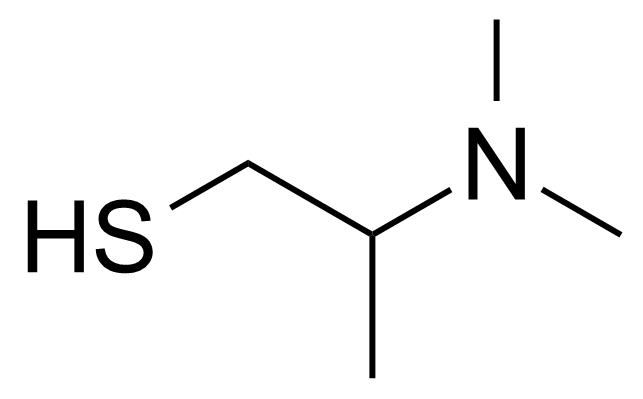 | [66338-45-2] | GEO-03243 |
| 3-(Dimethylamino)-1-propanethiol hydrochloride | 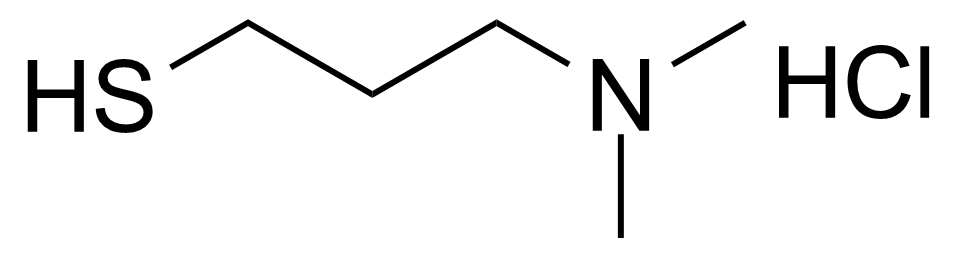 | [38048-81-6] | GEO-03245 |
| 2-(Dimethylamino)-1-propanethiol hydrochloride | 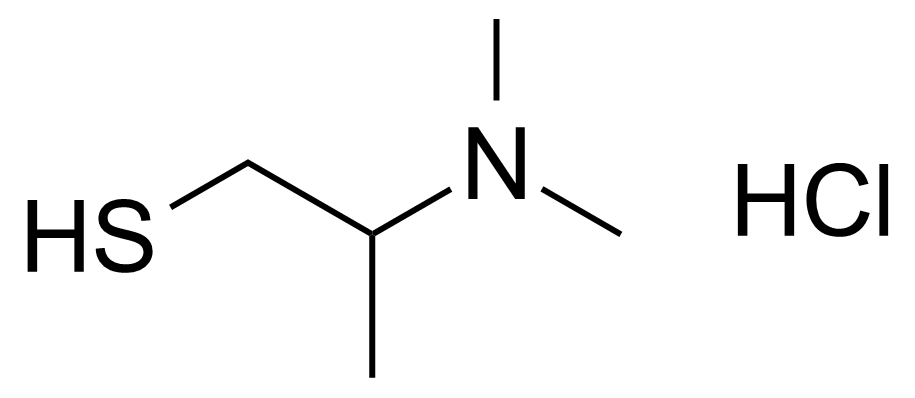 | [101724-24-7] | GEO-03244 |
| Dimethyl 2,5-dihydrothiophene-3,4-dicarboxylate | 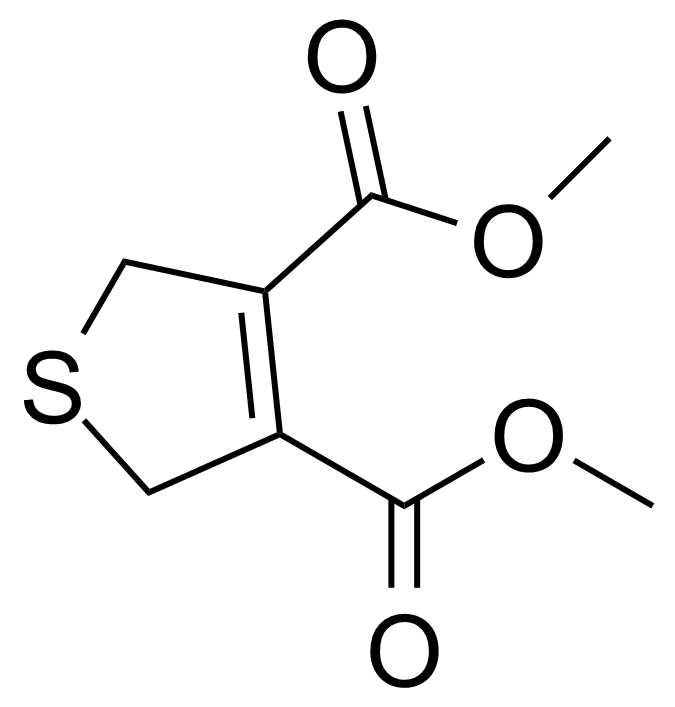 | [20946-32-1] | GEO-04024 |
| Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(5-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 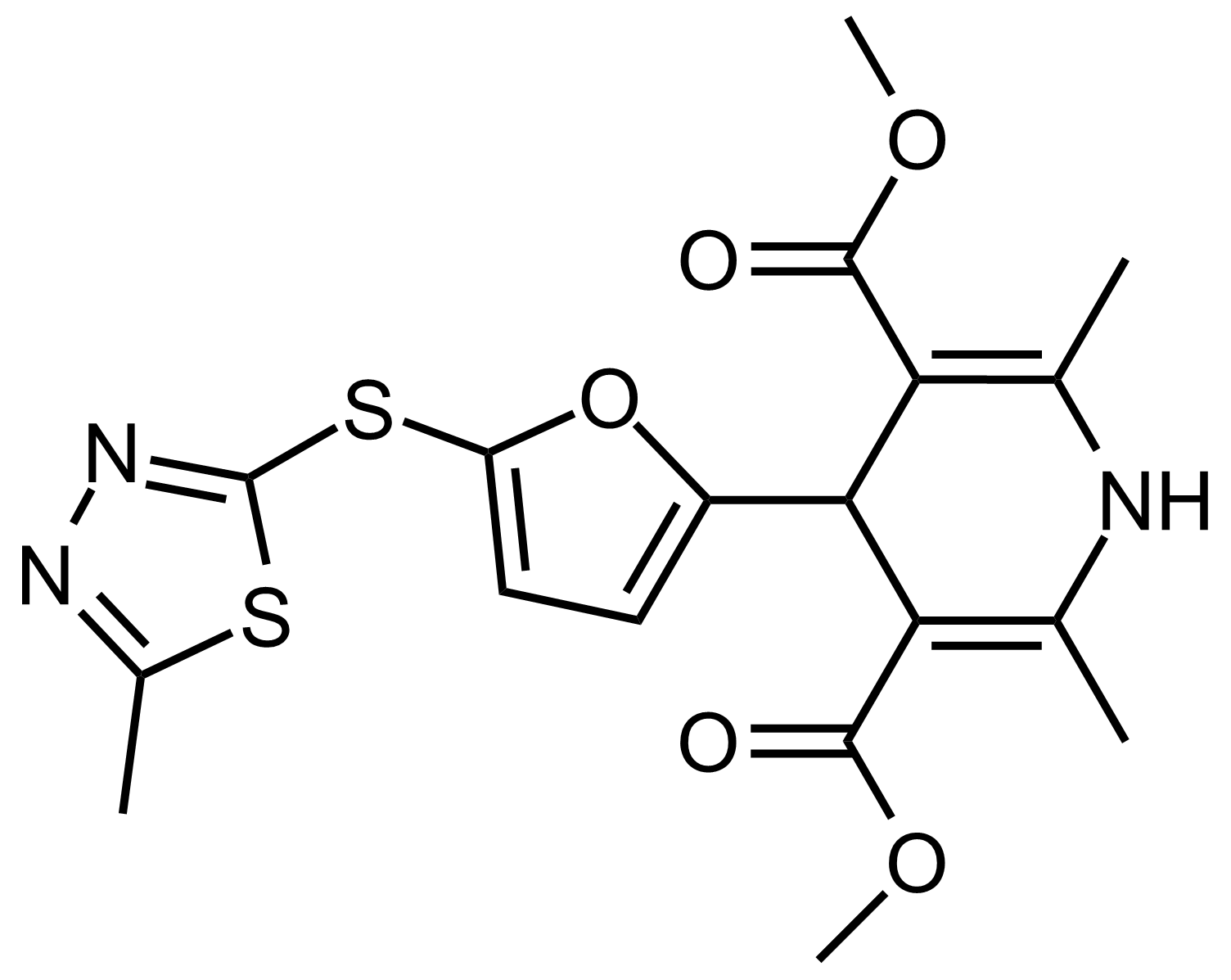 | N/A | GEO-03522 |
| Dimethyl 2,6-dimethyl-4-(5-(pyridin-2-ylthio)furan-2-yl)-1,4-dihydropyridine-3,5-dicarboxylate | 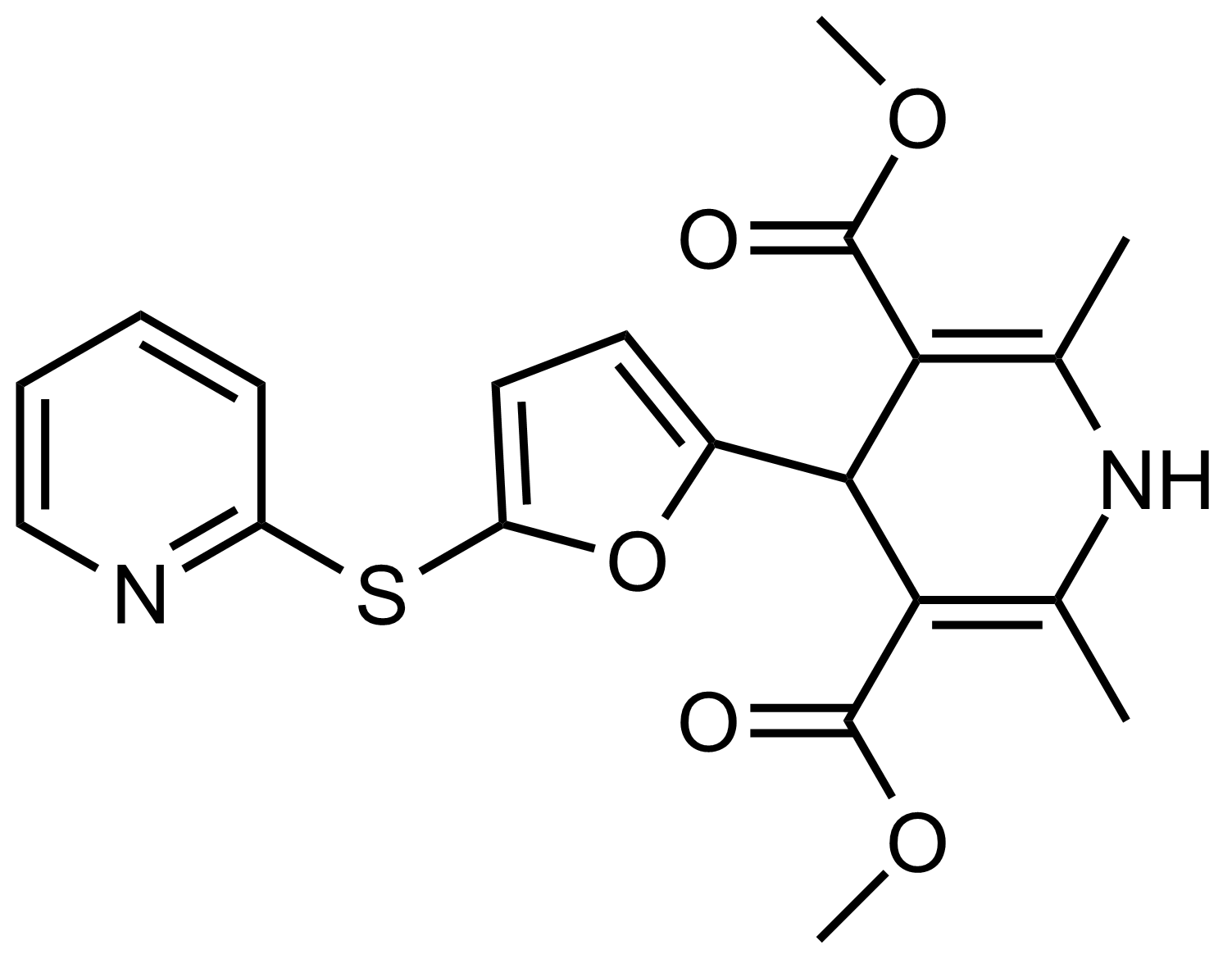 | N/A | GEO-03494 |
| 2-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]-ethanethiol | ![Structure of 2-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]-ethanethiol](https://georganics.sk/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/GEO-04479_2-11-Dimethylethyldimethylsilyloxy-ethanethiol.png) | [76855-57-7] | GEO-04479 |
| 4,5-Diphenyl-2-imidazolethiol | 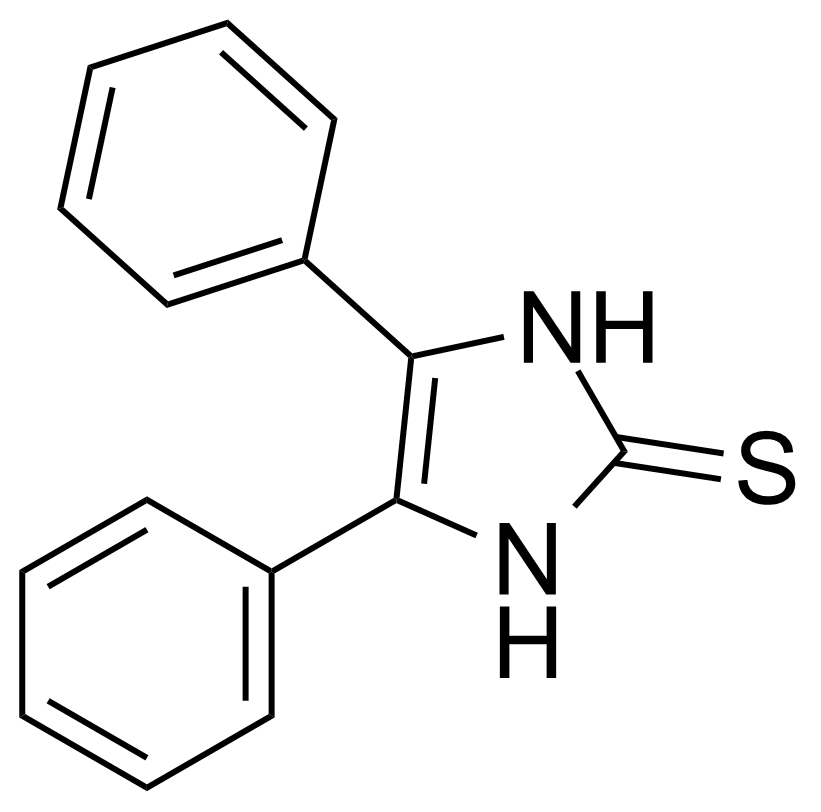 | [2349-58-8] | GEO-01241 |
| Ethyl 4-chloro-2-(methylthio)pyrimidine-5-carboxylate | 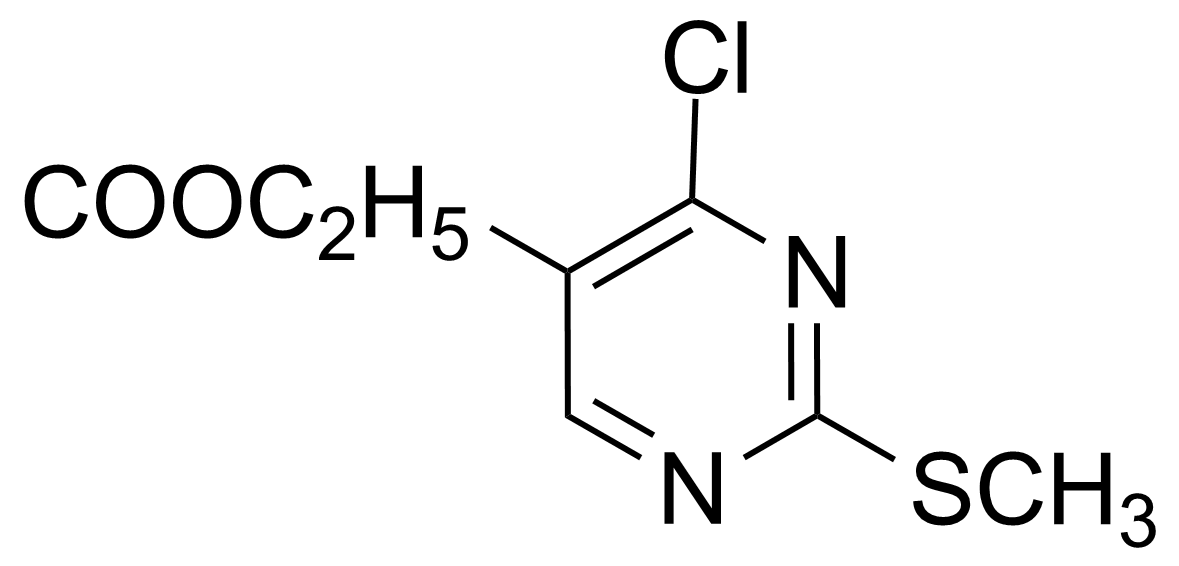 | [5909-24-0] | GEO-01330 |
| Ethyl 2,7,7-trimethyl-4-(5-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carboxylate | 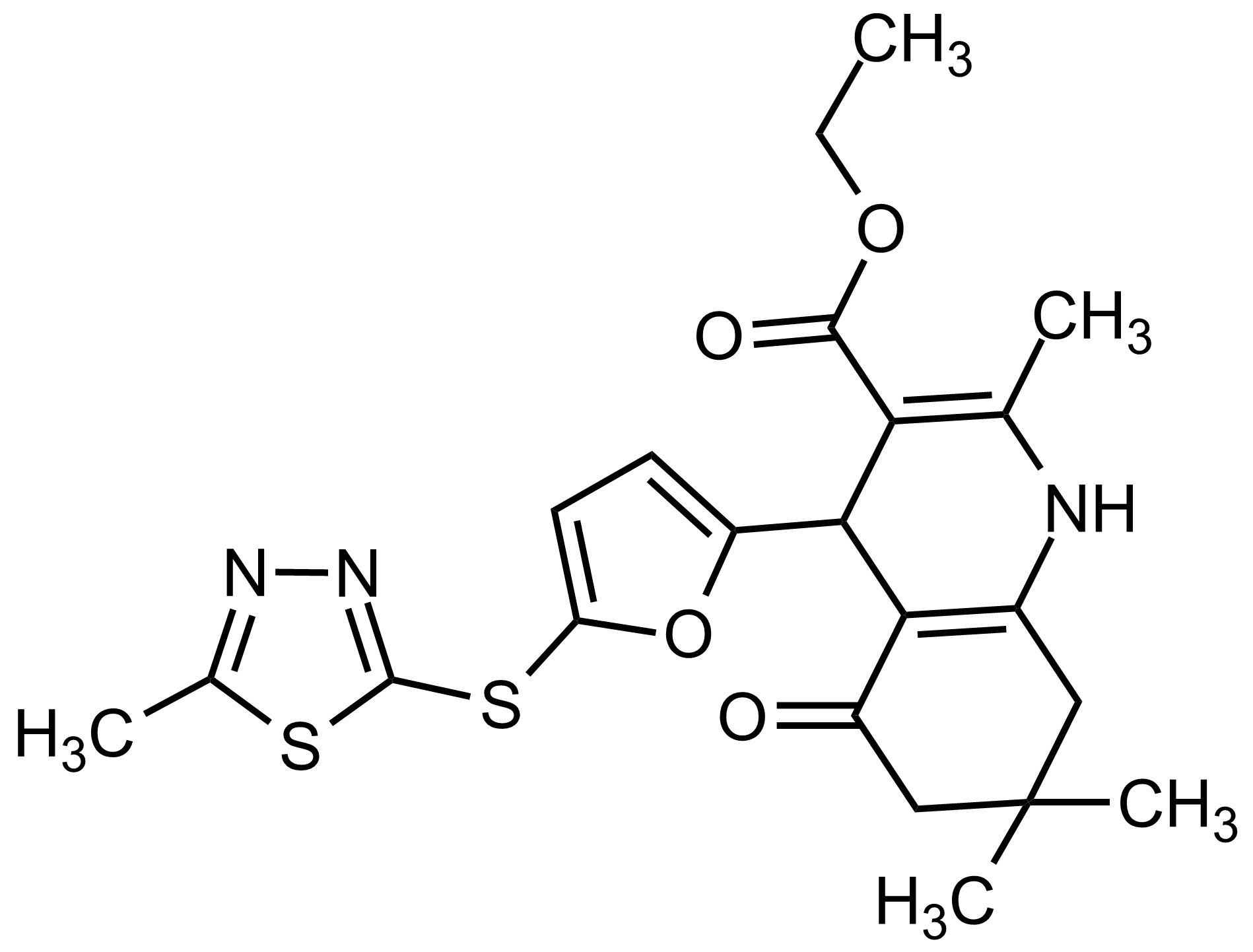 | N/A | GEO-03545 |
| (2-Fluorophenyl)methanethiol | 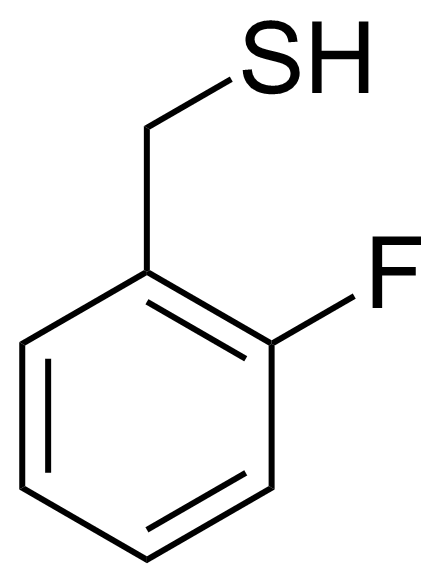 | [72364-46-6] | GEO-01428 |
| (4-Fluorophenyl)methanethiol | 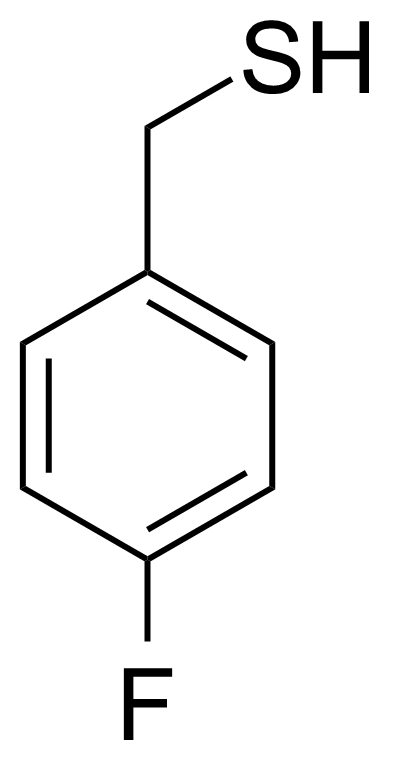 | [15894-04-9] | GEO-01430 |
| (3-Fluorophenyl)methanethiol | 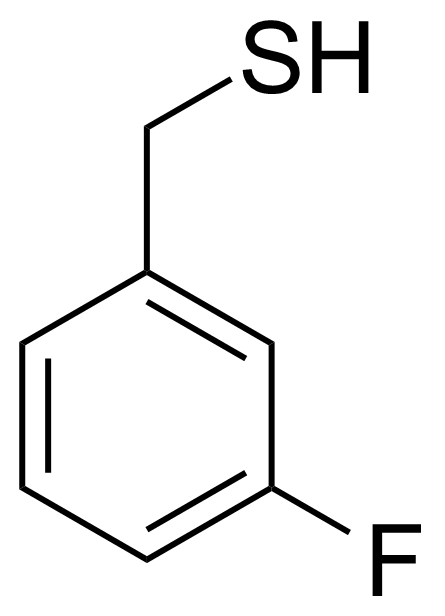 | [40096-23-9] | GEO-01429 |
| 6-Hydroxy-2-mercaptopurine | 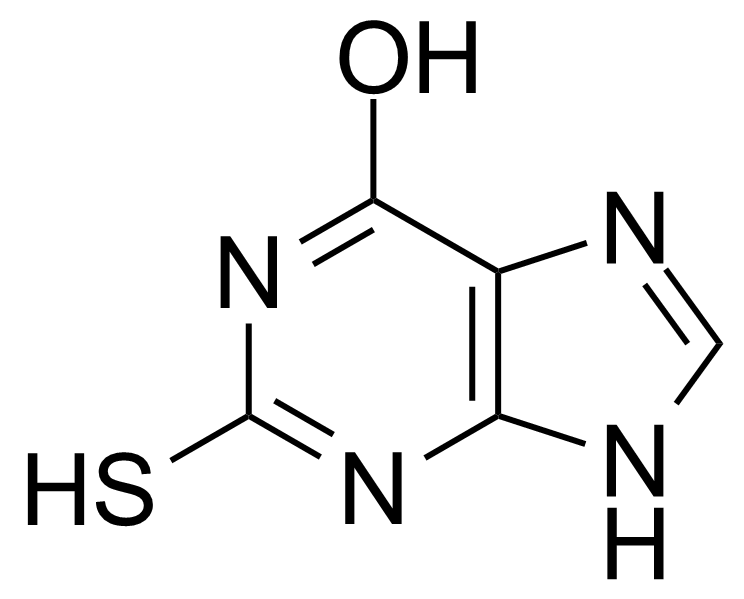 | [2487-40-3] | GEO-01523 |
| (Z)-2-Isocyano-3-(5-(pyridin-2-ylthio)furan-2-yl)acrylonitrile | 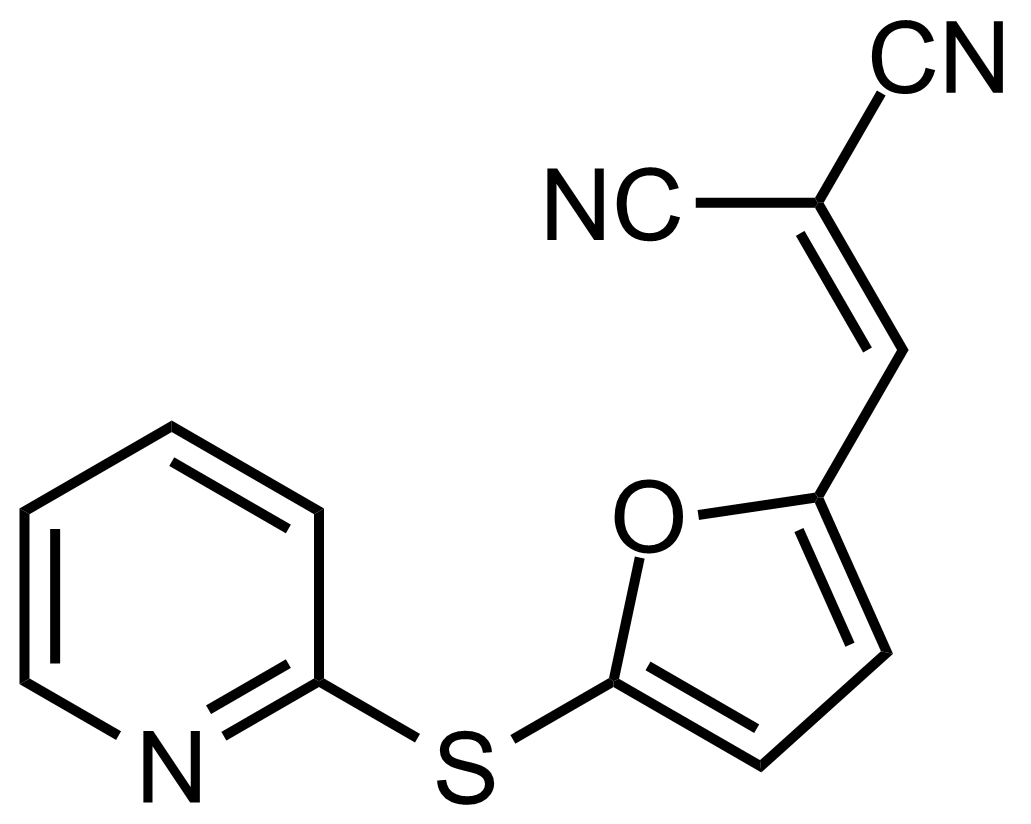 | N/A | GEO-03486 |
| 2-Mercapto-6-nitrobenzothiazole | 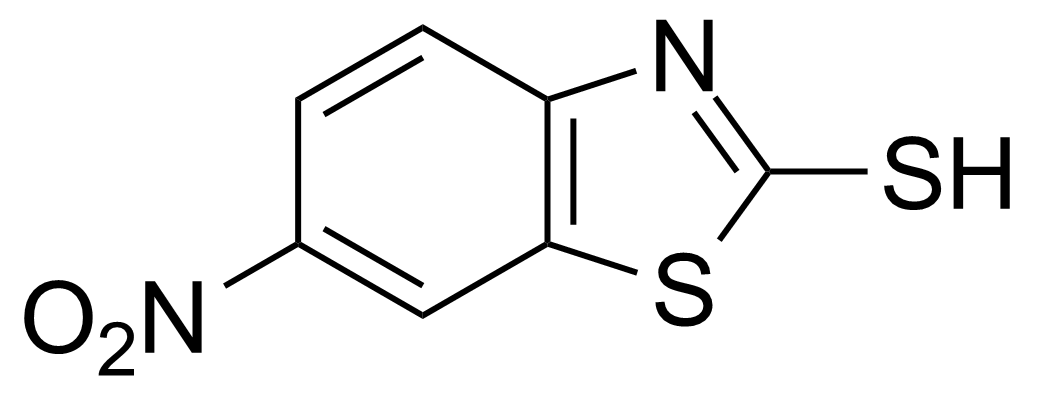 | [4845-58-3] | GEO-01654 |
| (E)-Methyl 2-cyano-3-(5-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)acrylate | 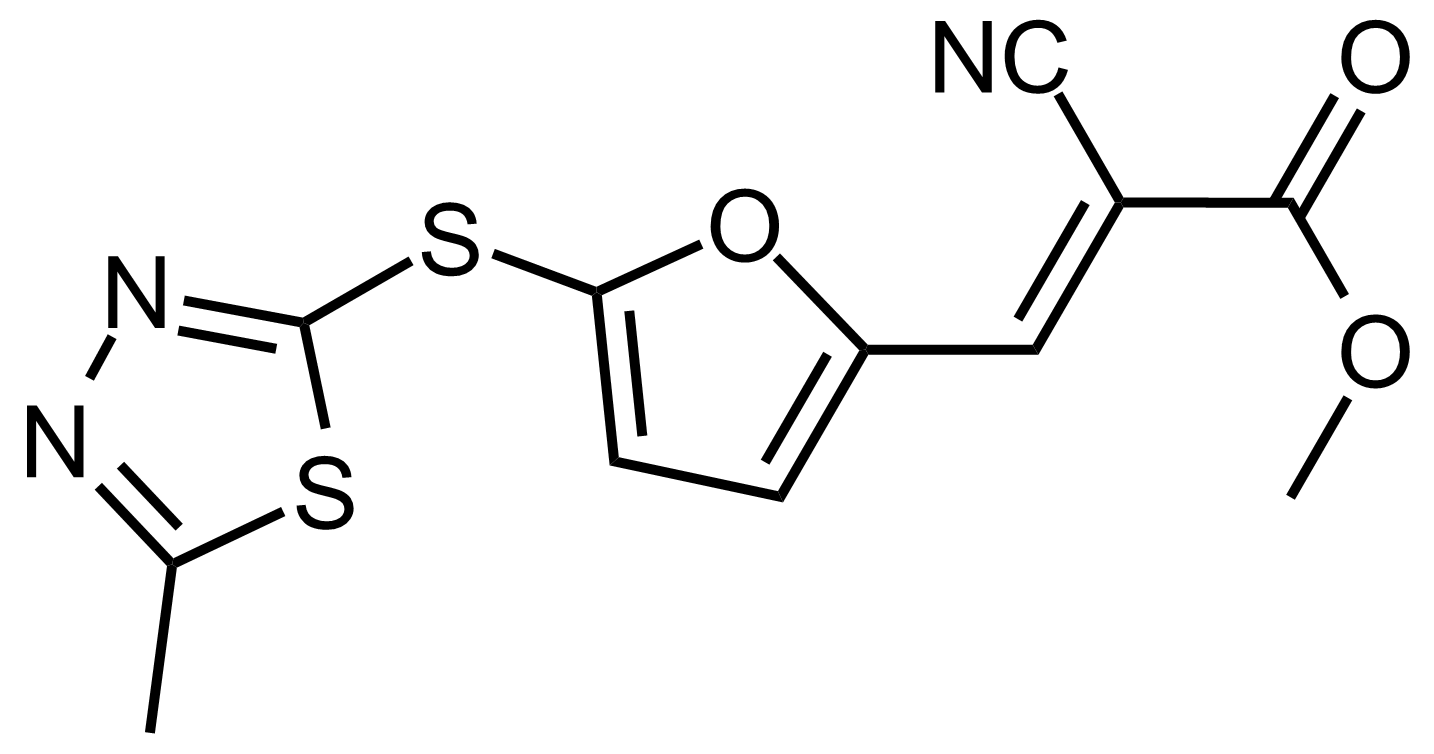 | N/A | GEO-03525 |
| (Z)-Methyl 2-cyano-3-(5-(pyridin-2-ylthio)furan-2-yl)acrylate | 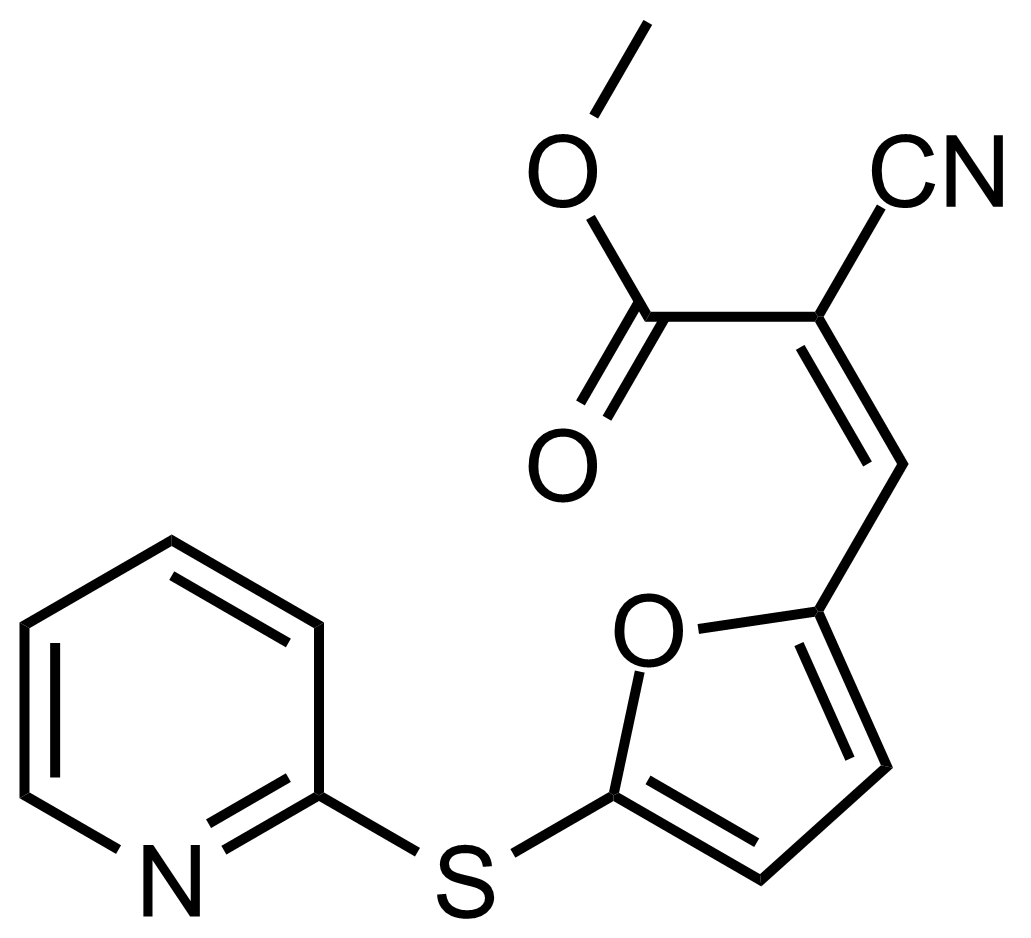 | N/A | GEO-03485 |
| (R)-2-Methylcysteine hydrochloride |  | [148766-37-4] | GEO-02622 |
| 3,4-(Methylenedioxy)thiophenol | 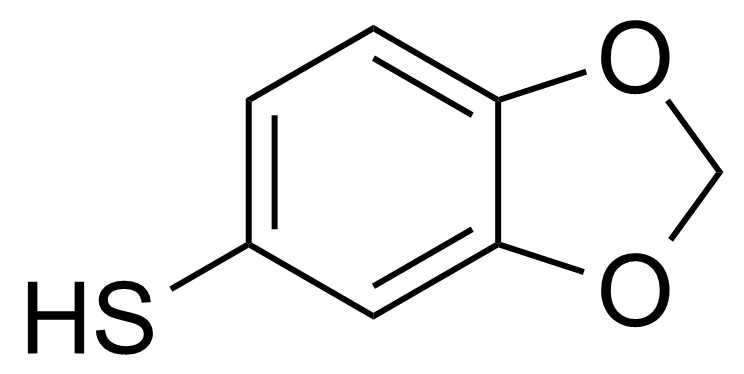 | [5274-08-8] | GEO-03999 |
| 6-Methyl-2-methylsulfanyl-1H-pyrimidin-4-one | 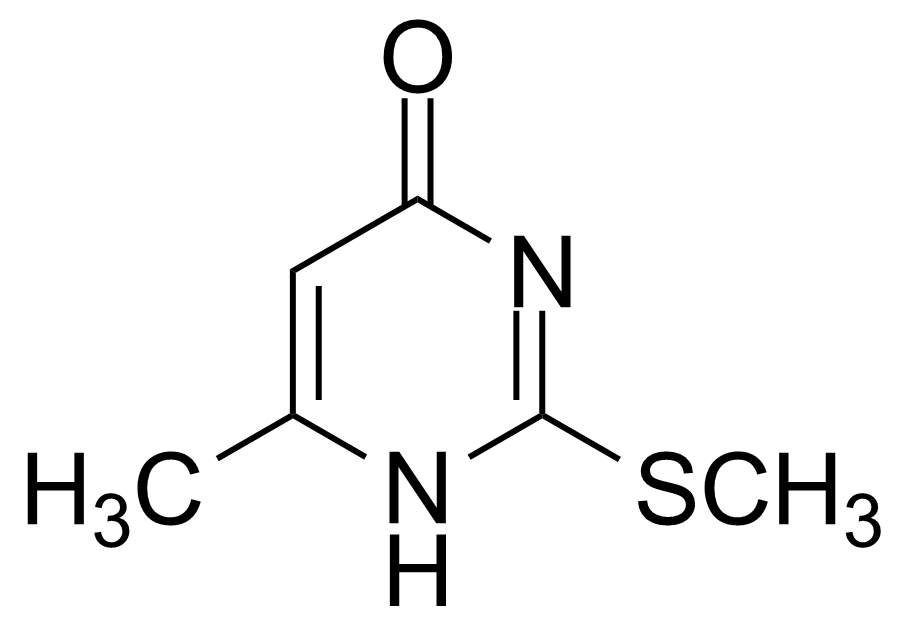 | [6328-58-1] | GEO-02802 |
| 5-((5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-carbaldehyde | 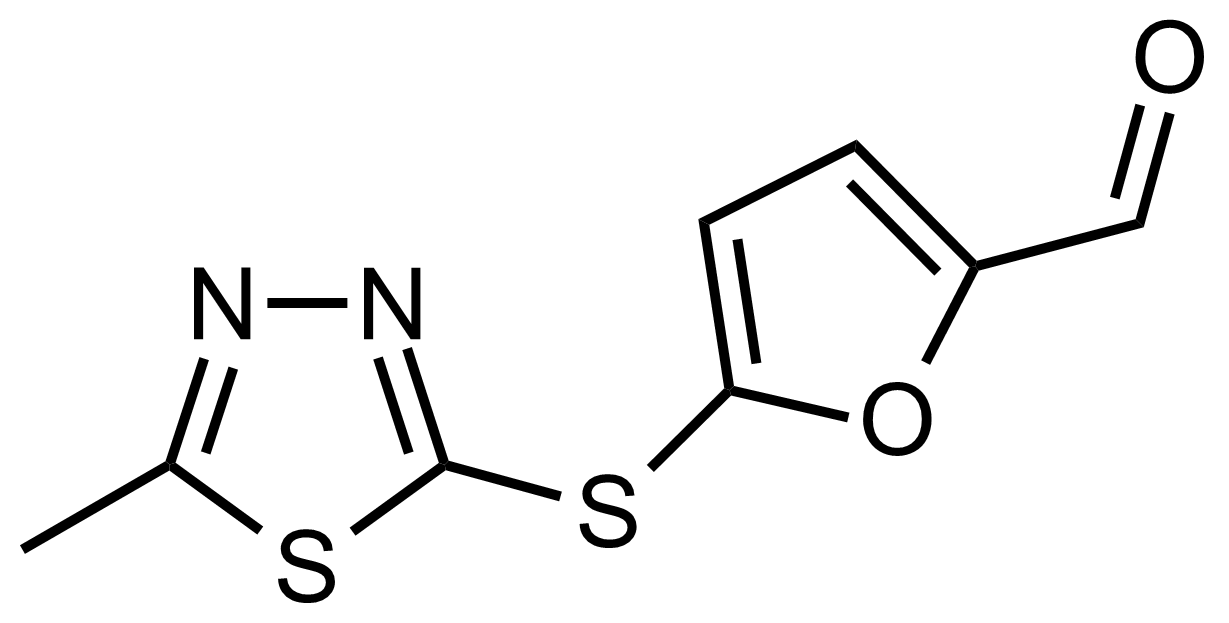 | N/A | GEO-03520 |
| (E)-3-(5-((5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)acrylic acid | 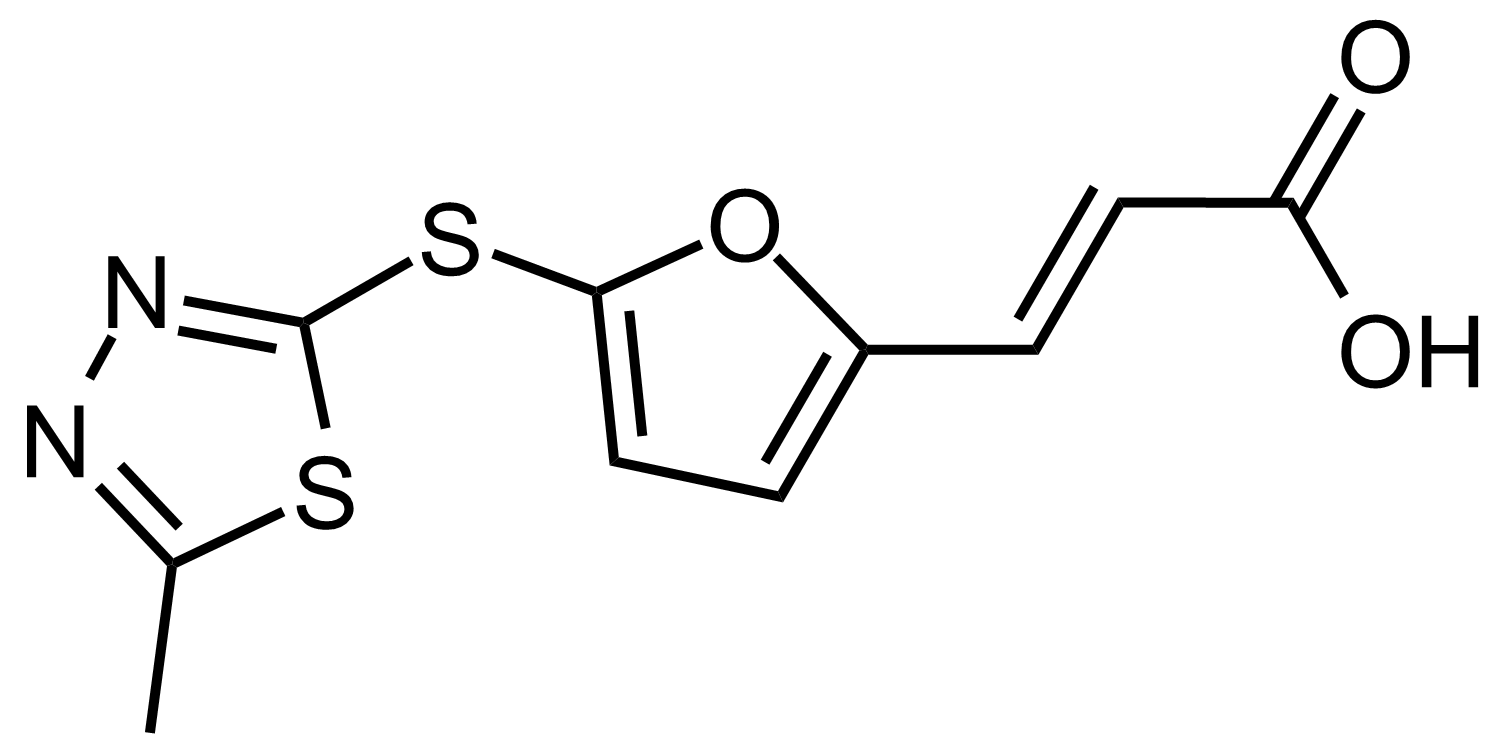 | N/A | GEO-03526 |
| 2-((5-((5-Methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)methylene)malononitrile | 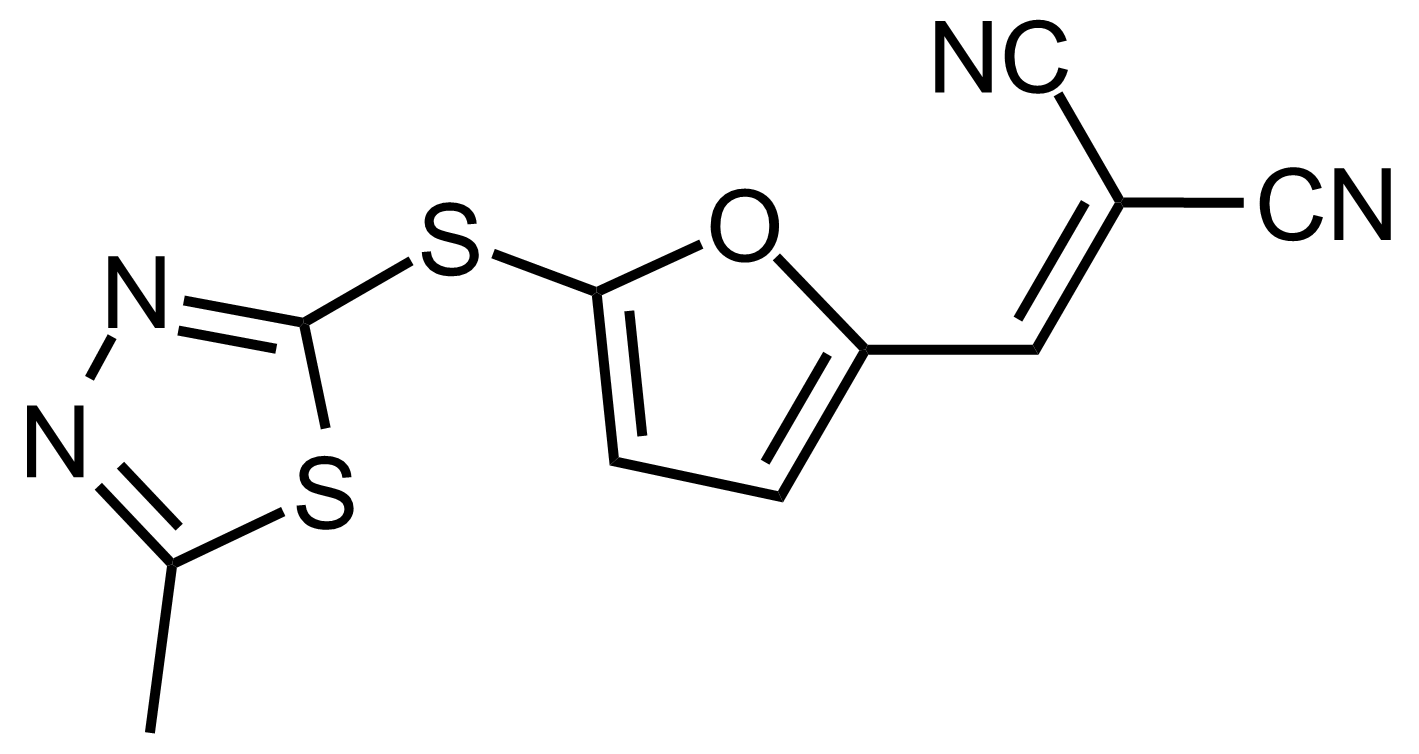 | N/A | GEO-03523 |
| 4′-(Methylthio)acetophenone | 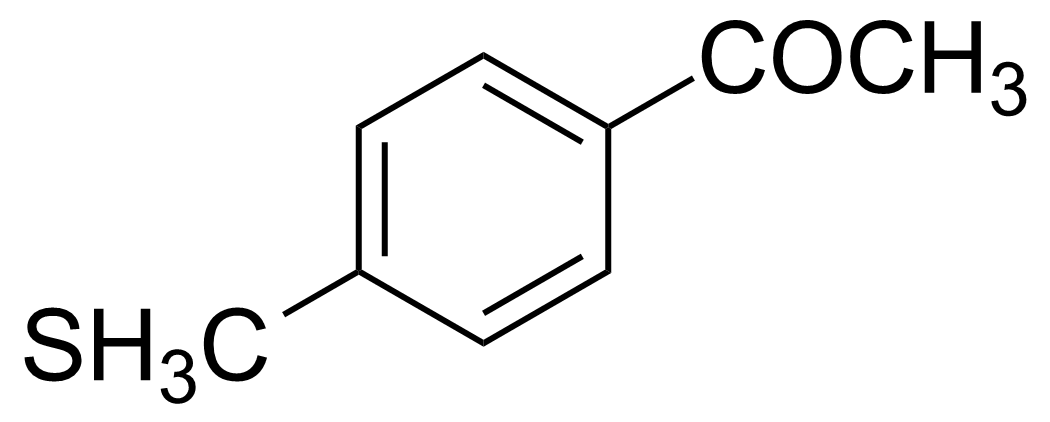 | [1778-09-2] | GEO-01947 |
| 2-Methylthio-4-aminouracil | 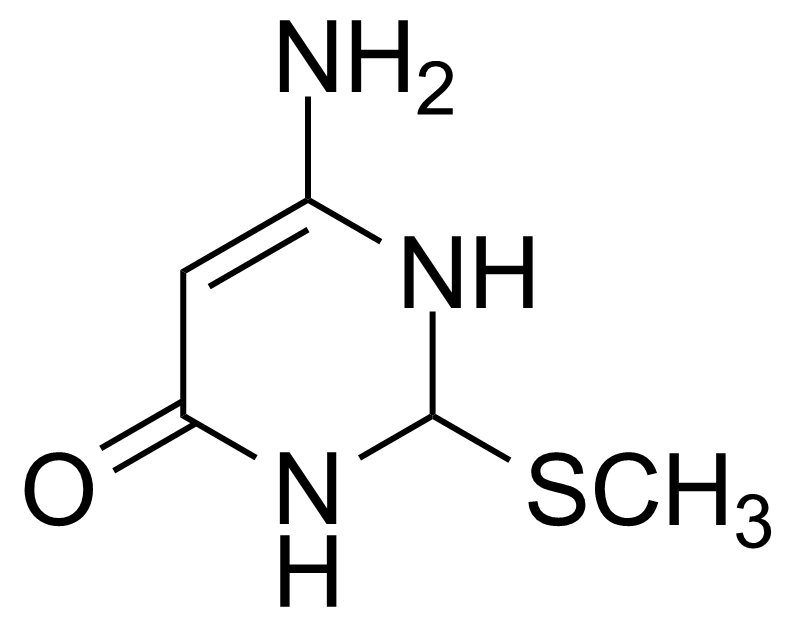 | [1195219-77-2] | GEO-03079 |
| 2-Methylthio-2-imidazoline hydriodide | 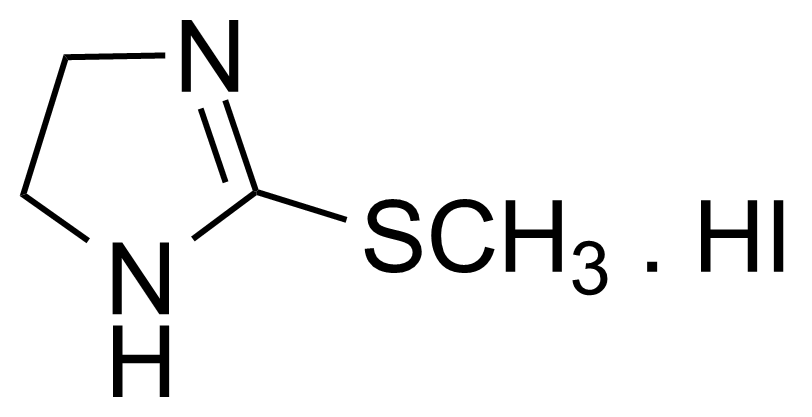 | [5464-11-9] | GEO-01949 |
| 4-(Methylthio)phenylacetic acid | 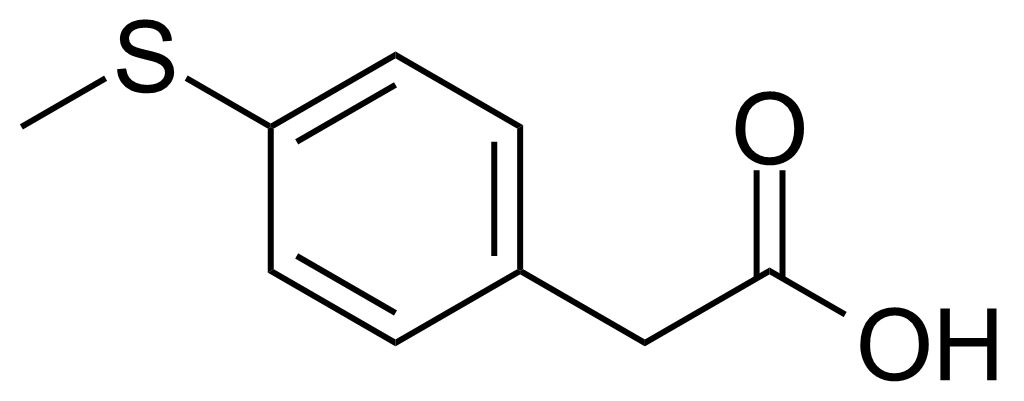 | [16188-55-9] | GEO-01963 |
| 3-(Methylthio)phenyl isocyanate | 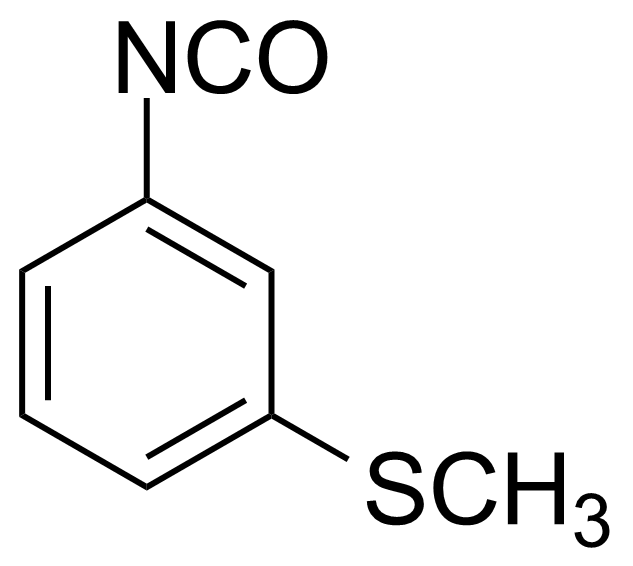 | [28479-19-8] | GEO-01964 |
| 4-(Methylthio)phenyl isocyanate | 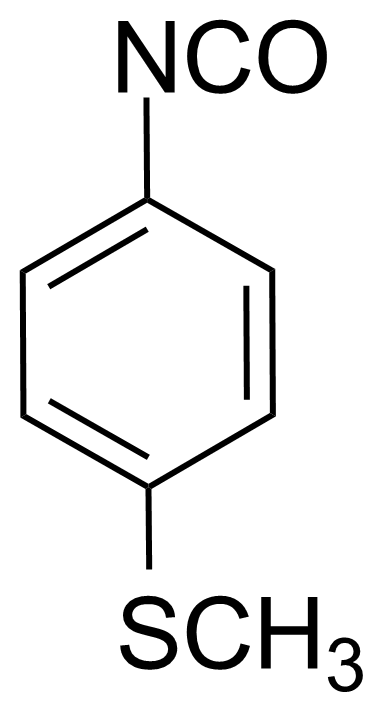 | [1632-84-4] | GEO-01965 |
| New | 4-(Methylthio)phenyl isothiocyanate | 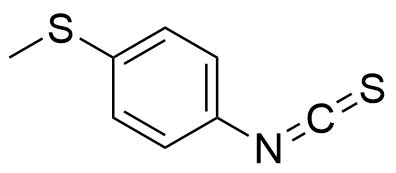 | [15863-41-9] | GEO-01967 |
| 3-(Methylthio)phenyl isothiocyanate | 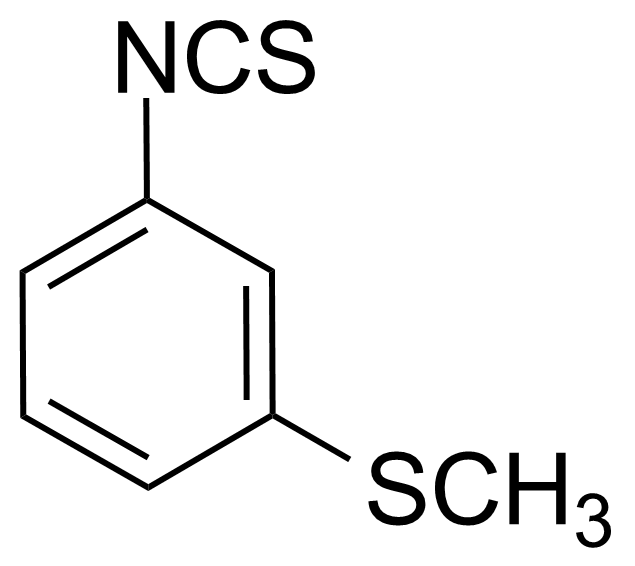 | [51333-80-3] | GEO-01966 |
| 3-(Methylthio)propanoic acid | 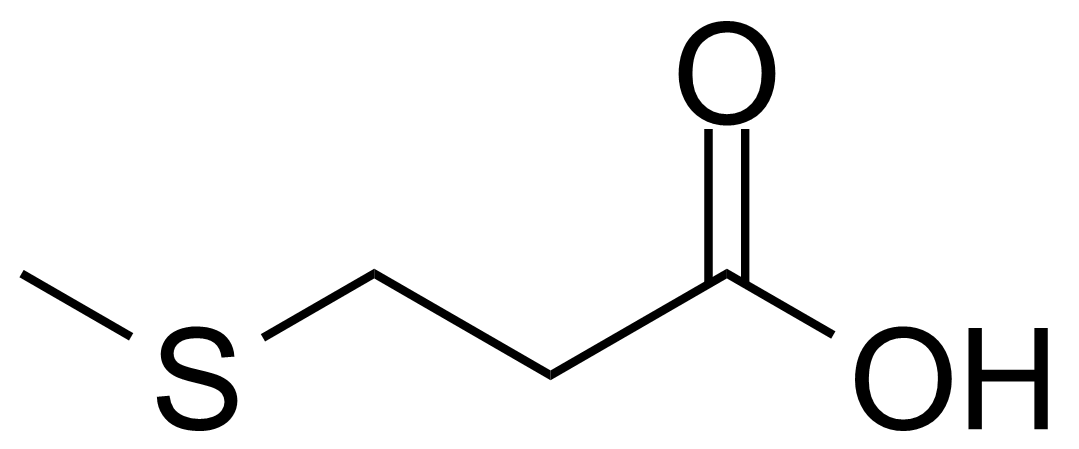 | [646-01-5] | GEO-01970 |
| 6-(Methylthio)pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(1H)-one | ![Structure of 6-(Methylthio)pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(1H)-one](https://georganics.sk/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/GEO-04340_6-Methylthiopyrimido54-dpyrimidin-41H-one.png) | [98550-19-7] | GEO-04340 |
| New | 5-Methylthio-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thiol | 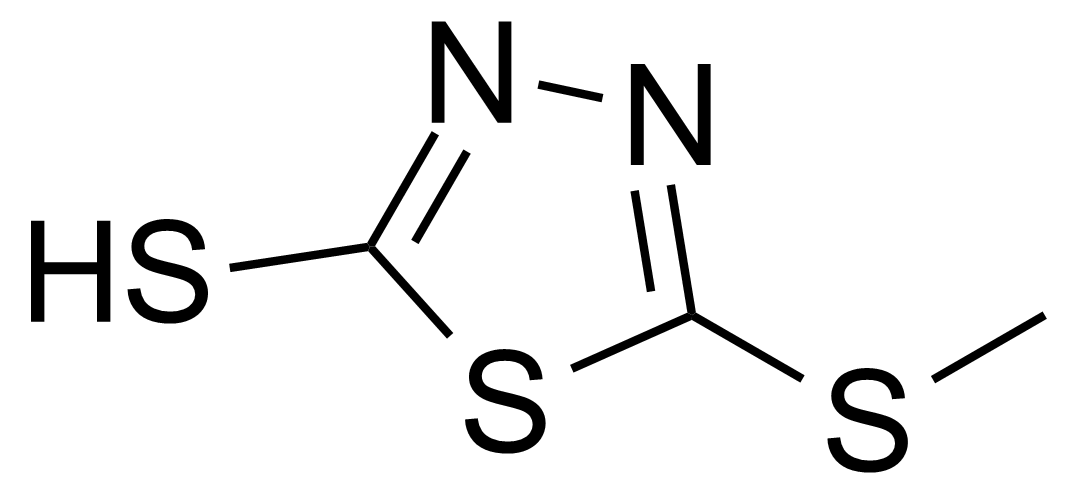 | [6264-40-0] | GEO-01973 |
| Phenylthiotrimethylsilane | 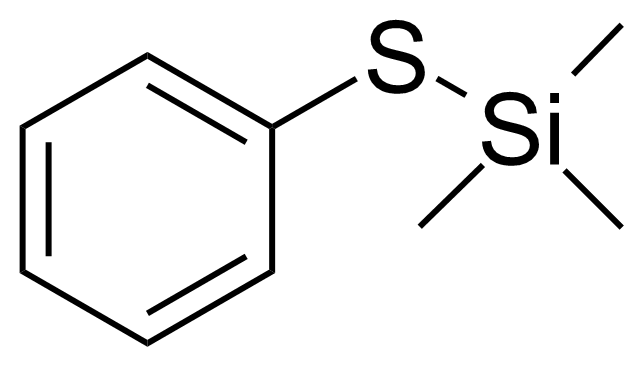 | [4551-15-9] | GEO-02142 |
| 5-(Pyridin-2-ylthio)furan-2-carbaldehyde | 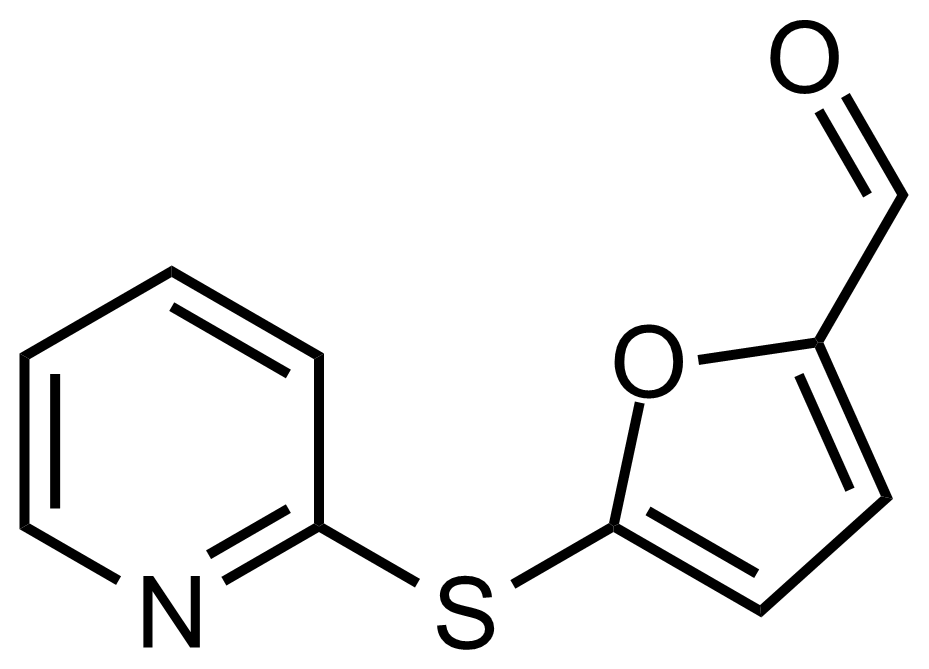 | [709635-68-7] | GEO-03484 |
| (2-Pyrimidylthio)acetic acid | 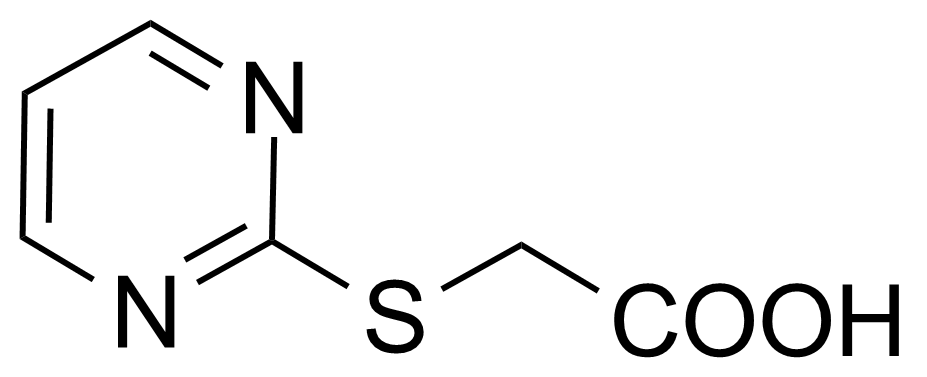 | [88768-45-0] | GEO-02198 |
| 3,3,6,6-Tetramethyl-9-(5-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)-3,4,6,7,9,10-hexahydroacridine-1,8(2H,5H)-dione | 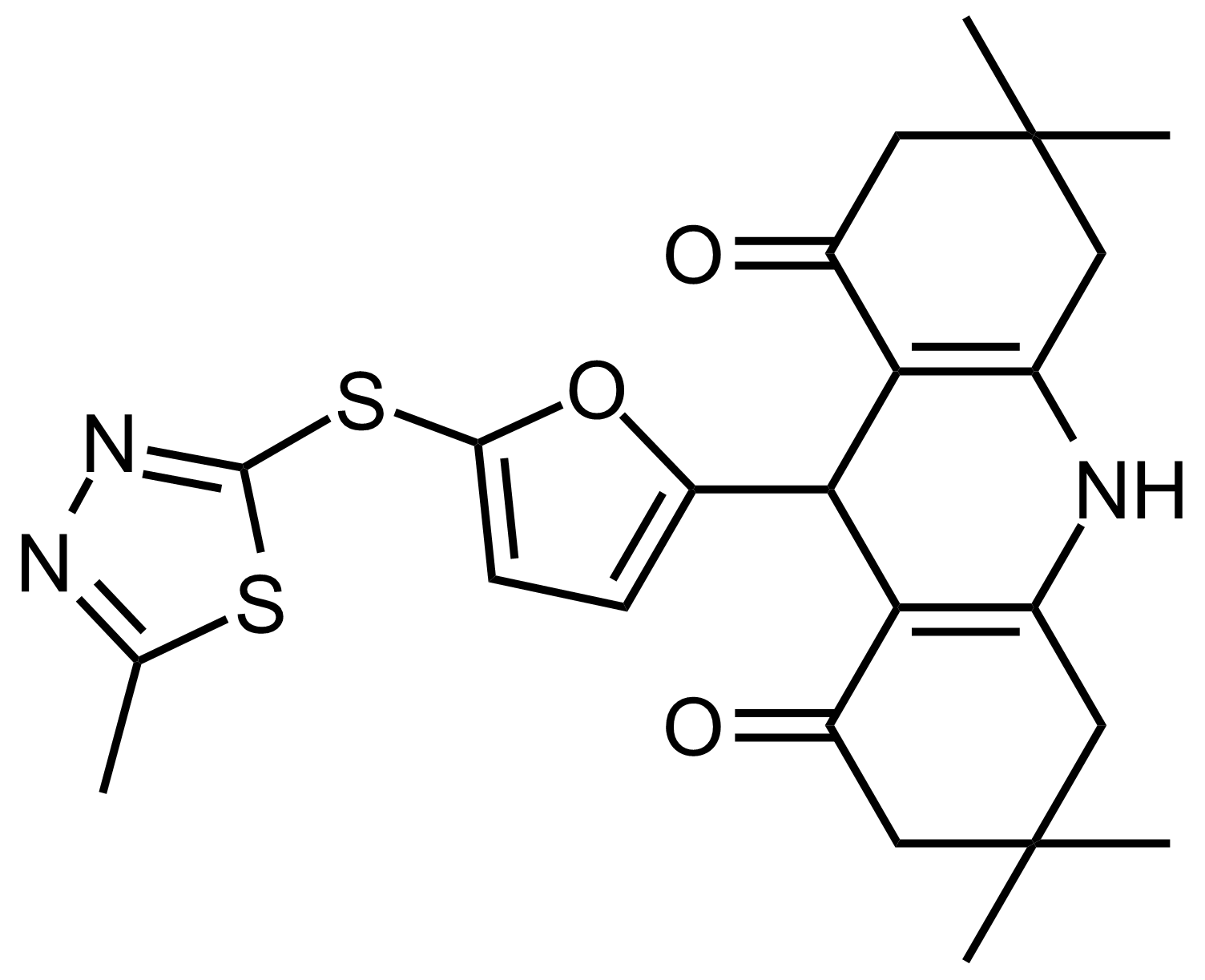 | N/A | GEO-03528 |
| 4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenylmethanethiol | 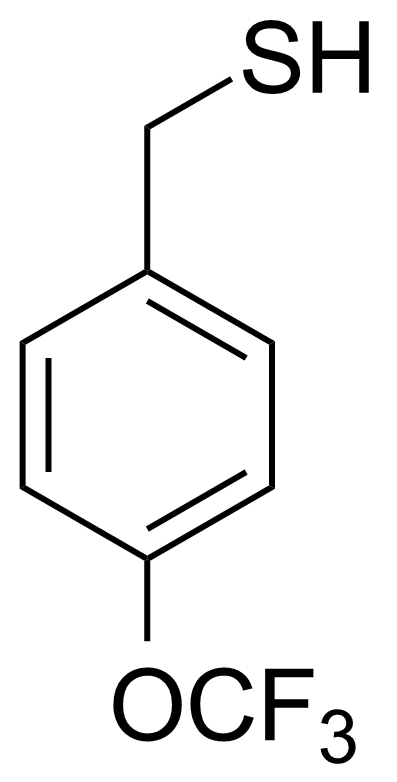 | [175278-03-2] | GEO-02375 |
| 3-(Trifluoromethyl)phenylmethanethiol | 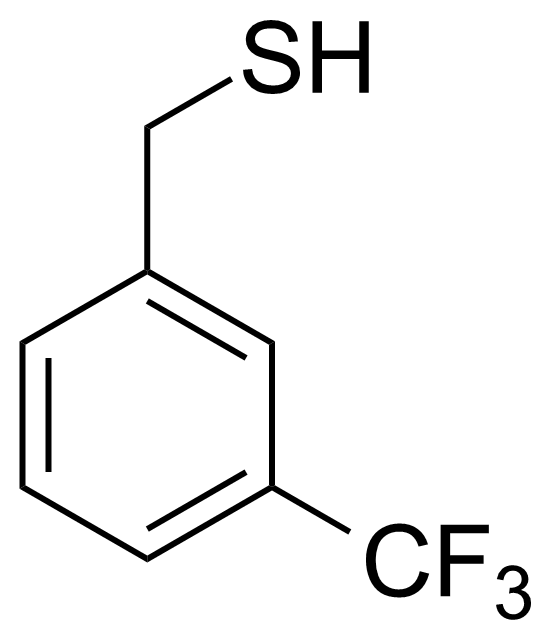 | [25697-55-6] | GEO-02383 |
| 2-(Trifluoromethyl)phenylmethanethiol | 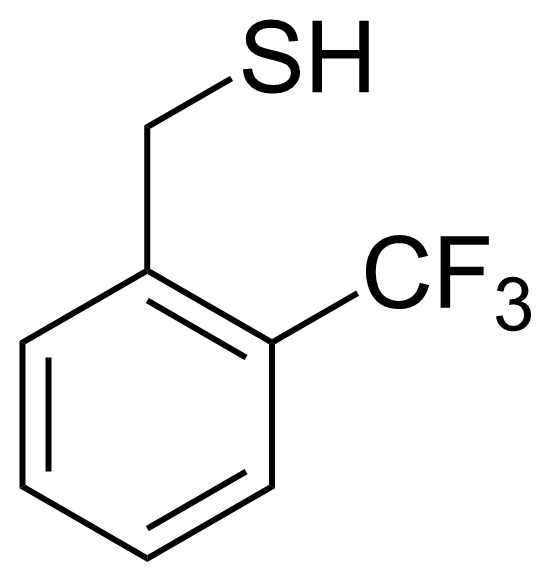 | [26039-98-5] | GEO-02382 |
| 4-(Trifluoromethyl)phenylmethanethiol | 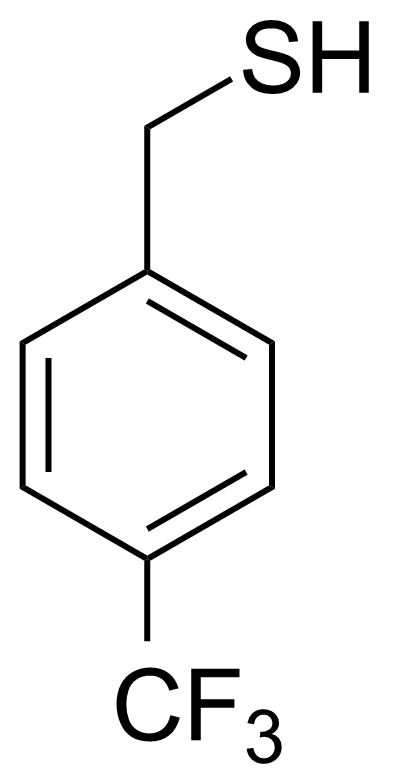 | [108499-24-7] | GEO-02384 |
| 2,7,7-Trimethyl-4-(5-((5-methyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)thio)furan-2-yl)-5-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydroquinoline-3-carbonitrile |  | N/A | GEO-03524 |







































![Structure of 2-[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)dimethylsilyl]oxy]-ethanethiol](https://georganics.sk/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/GEO-04479_2-11-Dimethylethyldimethylsilyloxy-ethanethiol.png)


























![Structure of 6-(Methylthio)pyrimido[5,4-d]pyrimidin-4(1H)-one](https://georganics.sk/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/GEO-04340_6-Methylthiopyrimido54-dpyrimidin-41H-one.png)









